List of countries by system of government
This is a list of sovereign states by their de jure systems of government, as specified by the incumbent regime's constitutional law.
This list does not measure the degree of democracy, political corruption, or state capacity of governments.
[1][2] The head of state is a monarch who normally only exercises their powers with the consent of the government, the people and/or their representatives (except in emergencies, e.g. a constitutional crisis or a political deadlock).
In presidential systems a president is the head of government, and is elected and remains in office independently of the legislature.
There is generally no prime minister, although if one exists, in most cases they serve purely at the discretion of the president.
The following countries have presidential systems where the post of prime minister (official title may vary) exists alongside that of the president.
In a semi-presidential republic a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature.
The prime minister is the nation's active executive, but the monarch still has considerable political powers that can be used at their own discretion.
Specifically, monarchies in which the monarch's exercise of power is unconstrained by any substantive constitutional law.
States in which political power is by law concentrated within one political party whose operations are largely fused with the government hierarchy (in contrast to states where a multi-party system formally exists, but this fusion is achieved anyway through election fraud or underdeveloped multi-party traditions).
A committee of the nation's military leaders controls the government for the duration of a state of emergency.
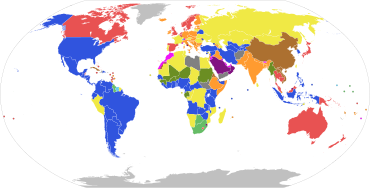
Parliamentary systems : Head of government is elected or nominated by and accountable to the legislature
Presidential system : Head of government (president) is popularly elected and independent of the legislature
Hybrid systems:
Other systems:
Note: this chart represents the de jure systems of government, not the de facto degree of democracy.