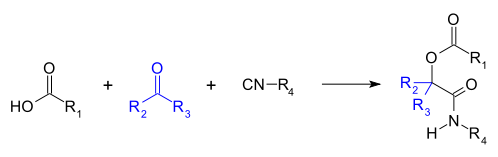Passerini reaction
[6][8][9] As isocyanides exhibit high functional group tolerance, chemoselectivity, regioselectivity, and stereoselectivity, the Passerini reaction has a wide range of synthetic applications.
A concerted mechanism, seen in SN2 and Diels−Alder reactions, is theorized to occur when the Passerini reagents are present at high concentration in aprotic solvents.
[14][15] In polar solvents, such as methanol or water, the carbonyl is protonated before nucleophilic addition of the isocyanide, affording a nitrilium ion intermediate.
[16][17] To facilitate the Passerini reaction between bulky, sterically hindered reagents, a vortex fluidic device can be used to induce high shear conditions.
These conditions emulate the effects of high temperature and pressure, allowing the Passerini reaction to proceed fairly quickly.
[20] Macromolecules that have been produced with this reaction include macroamides, macrocyclic depsipeptides, three-component dendrimers and three-armed star branched mesogen core molecules.
[12] The Passerini reaction has synthesized α-Acyloxy carboxamides that have demonstrated activity as anti-cancer medications along with functionalized [C60]-fullerenes used in medicinal and plant chemistry.