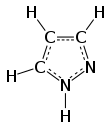
Pyrazole
The two C-N distances are similar, both near 1.33 Å[4] Pyrazoles are also a class of compounds that have the ring C3N2 with adjacent nitrogen atoms.
[9] In a classical method developed by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1898, pyrazole was synthesized from acetylene and diazomethane.
[14][15] In medicine, derivatives of pyrazole are widely used,[16] including celecoxib and similar COX-2 inhibitors, zaleplon, betazole, and CDPPB.
[17] The pyrazole ring is found within a variety of pesticides as fungicides, insecticides and herbicides,[16] including fenpyroximate, fipronil, tebufenpyrad and tolfenpyrad.
[18] Pyrazole moieties are listed among the highly used ring systems for small molecule drugs by the US FDA[19] 3-(Difluoromethyl)-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid is used in the manufacture of six commercial fungicides which are inhibitors of succinate dehydrogenase.