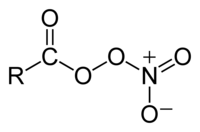
Peroxyacyl nitrates
They are nitrates produced in the thermal equilibrium between organic peroxy radicals by the gas-phase oxidation of a variety of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), or by aldehydes and other oxygenated VOCs oxidizing in the presence of NO2.
[1][2][3] They are good markers for the source of VOCs as either biogenic or anthropogenic, which is useful in the study of global and local effects of pollutants.
[6]: 2680 Since they dissociate quite slowly in the atmosphere into radicals and NO2, PANs are able to transport these unstable compounds far away from the urban and industrial origin.
The composition of PANs in a particular region depends heavily on which hydrocarbons are present in the atmosphere, with the exception of peroxyacetyl nitrate, which is able to be produced from a range of precursors.
PANs are mutagenic,[7] and are considered potential contributors to the development of skin cancer.