Petasis reaction
As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.
[8][9] A wide variety of functional groups including alcohols, carboxylic acids, and amines are tolerated in the Petasis Reaction.
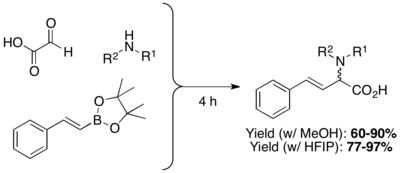
The highly polar protic solvents Hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) can shorten reaction time and improve yield.
Possible substrate scope includes thienyl, pyridyl, furyl, and benzofuranyl, 1-naphthyl, and aryl groups with either electron-donating or electron-withdrawing substituent.
The reaction is carried out under harsh conditions (24-hr reflux in 1,4-dioxane), but the resultant carboxylic acid is obtained in reasonable yield.
[3] Diastereoselectivity may arise from the reaction of the more stable (and, in this case, more reactive) conformation of the ate complex, where 1,3 allylic strain is minimized.
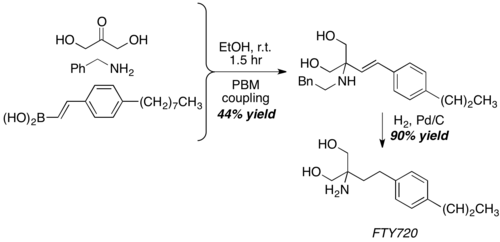
[20][21][22] With dihydroxyacetone, a somewhat unconventional aldehyde equivalent, Petasis reaction give the core structure of FTY720, a potent immunosuppressive agent.
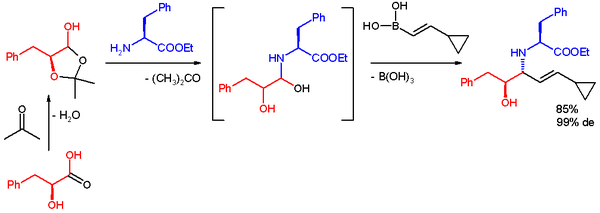
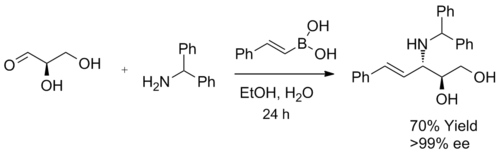
It is used as the equivalent of α-hydroxyl aldehydes with pre-existing chirality, and the aminopolyol product is usually furnished with moderate to good yield, with excellent selectivity.
Chiral benzyl amines,[24] 2-substituted pyrrolidines,[25] and 5-substituted 2-morpholinones[26][27] have been shown to induce good to excellent diastereomeric excess under different Petasis reaction conditions.
The key acyclic precursor to deoxycastanospermine (A) is formed first by condensing vinyl boronic ester 1 with Cbz-protected hydroxy-pyrrolidine 2 with a PBM coupling, followed by dihydroxylation and TBS protection.
Chiral α-amino acids with various functionalities are conveniently furnished by mixing alkenyl diethyl boronates, secondary amines, glyoxylates, and chiral biphenol catalyst in toluene in one-pot:[32] This reaction tolerates a wide range of functionalities, both on the sides of alkenyl boronates and the secondary amine: the electron-richness of the substrates does not affect the yield and enantioselectivity, and sterically demanding substrates (dialkylsubstituted alkenyl boronates and amines with α-stereocenter) only compromise enantioselectivity slightly.
[32] More recently, Yuan with coworkers from Chengdu Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Science combined both approaches (chiral thiourea catalyst and chiral biphenol) in a single catalyst, reporting for the first time the catalytic system that is capable of performing enantioselective Petasis reaction between salicylaldehydes, cyclic secondary amines and aryl- or alkenylboronic acids:[33] In one application the Petasis reaction is used for quick access to a multifunctional scaffold for divergent synthesis.
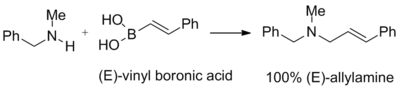
The reaction takes place in ethanol at room temperature to give the product, an anti-1,2-amino alcohol with a high diastereomeric excess.
In a recent report, Schaus and co-workers reported that syn amino alcohol can be obtained with the following reaction condition, using a chiral dibromo-biphenol catalyst their group developed:[35] Although the syn vs. anti diastereomeric ratio ranges from mediocre to good (1.5:1 to 7.5:1), the substrate scope for such reactions remain rather limited, and the diastereoselectivity is found to be dependent on the stereogenic center on the amine starting material.
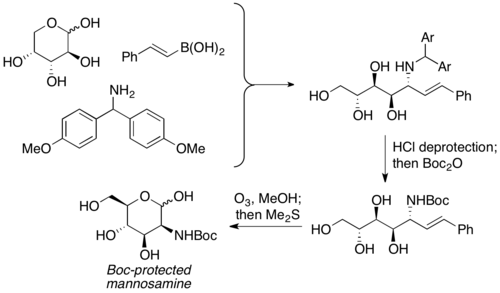
[35] Beau and coworkers assembled the core dihydropyran framework of zanamivir congeners via a combination of PBM reaction and Iron(III)-promoted deprotection-cyclization sequence.
Selective opening of the oxazoline portion of the dihydropyran intermediate 4 with water or timethylsilyl azide then furnish downstream products that have structures resembling the Zanamivir family members.
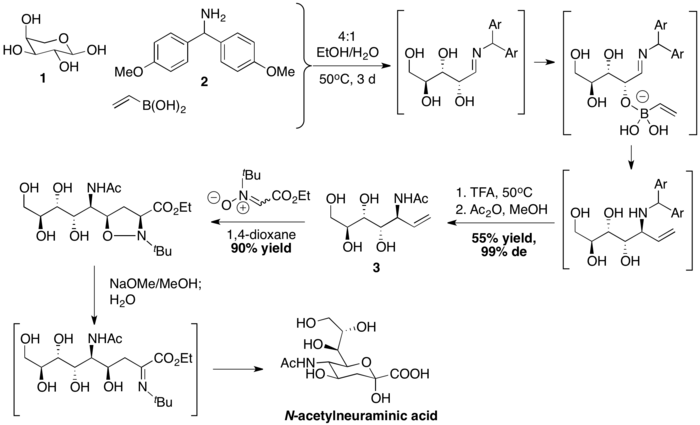
Afterwards, the sequence of dipolar cycloaddition, base-mediated N–O bond breakage and hydrolysis then complete the synthesis of N-acetylneuraminic acid.










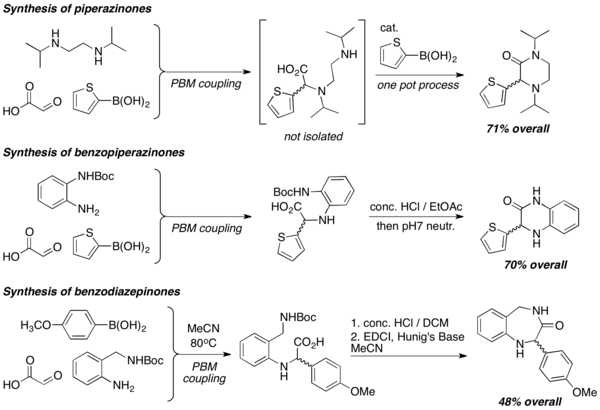



![Deoxycastanospermine synthesis.[30]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/da/Deoxycastanospermine_synthesis.png/600px-Deoxycastanospermine_synthesis.png)