Portuguese people
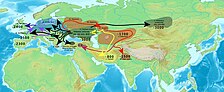
[115][116][106][107] Other minor – as well as later – influences include small Viking settlements between the 9th and 11th centuries, made by Norsemen who raided coastal areas mainly in the northern regions of Douro and Minho.
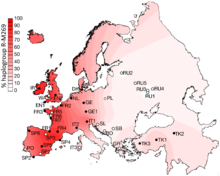
Y-chromosome and mtDNA data suggest that modern Portuguese trace a proportion of these lineages to the paleolithic peoples who began settling the European continent at the end of the last glaciation around 45,000 years ago.
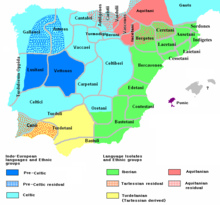
The Lusitanians (or Lusitānus – singular – Lusitani – plural – in Latin) were an Indo-European people living in the Western Iberian Peninsula long before it became the Roman province of Lusitania (modern Portugal, Extremadura and part of Salamanca).
[144] The first area settled by the Lusitanians was probably the Douro Valley and the region of Beira Alta; they subsequently moved south, and expanded on both sides of the Tagus river, before the Roman conquest.
However, when Audax, Ditalcus and Minurus returned to receive their reward, Consul Quintus Servilius Caepio ordered their execution, declaring, "Rome does not pay traitors".Viriathus[153] was the first Portuguese 'national hero' .
Although the country began as a county, after the Battle of São Mamede on 24 June 1128 Portugal was officially recognised as a kingdom via the Treaty of Zamora and the papal bull Manifestis Probatum of Pope Alexander III.
where the ending -es means "son of"), locative (Gouveia, Guimarães, Lima, Maia, Mascarenhas, Serpa, Montes, Fonseca, Barroso), religious origin (Cruz, Reis, De Jesus, Moysés, Nascimento), occupational (Carpinteiro (carpenter), Malheiro (wool-maker, thresher), Jardineiro (gardener), or derived from physical appearance (Branco (white), Trigueiro (brown, tanned), Louraço (blond).
In some previous Asian colonies (India, Malaysia, East Timor) alternative spellings are used such as 'D'Souza, Desouza, De Cunha, Ferrao, Dessais, Balsemao, Conceicao, Gurjao, Mathias, Thomaz.
[240] Descendants of Portuguese Sephardi Jews established many communities around the world, including in significant numbers in Israel, the Netherlands, the United States, France, Venezuela, Brazil and Turkey.
Although officially neutral, the Portuguese regime at that time, Estado Novo, aligned with Germany's ideology and failed to protect its citizens and other Jewish people living overseas.
[280][281] Mathias de Sousa, who was potentially a Sephardic Jew of mixed African background, is believed to be the first documented Portuguese resident of colonial United States.
As part of a larger system of low-wage labour, about 2,500 Portuguese left for Antigua and Barbuda[299] (where, more than 1,000 people still speak the language),[300] 30,000 to Guyana (4.3% of the population in 1891)[301] and another 2,000 settled in Trinidad and Tobago[302][303][304] between the mid-1800s and the mid-1900s.
[324] Notable members of the community include activist Ada Bello, businesswoman Alexis Victoria Yeb, former Nicaraguan First Lady Lila Teresita Abaunza and Felipa Colón de Toledo.
Interestingly, migration to Andorra - where, although Catalan is the official language, French is widely spoken - made the Portuguese the third largest ethnic group in the state, after Andorrans and Spaniards.
[362][363] From the 1960s, Brazil's economic stagnation, French efforts to attract Portuguese workers, and António de Oliveira Salazar's dictatorship and the colonial wars were factors that contributed to 1,000,000 people migrating to France from 1960 to 1974.
[376] Notable Portuguese Swiss include snooker player Alexander Ursenbacher, models Pedro Mendes and Nomi Fernandes, actress Yaël Boon and Olympic medalist Stéphane Lambiel.
[405] A large, community-based multicenter autosomal study considered representative samples from three urban communities Salvador, Bambuí, and Pelotas, estimated European, mostly Iberian, ancestry to be 42.4%, 83.8% and 85.3%, respectively.
[408][409][410][411] Notable Portuguese Australians include Naomi Sequeira, Kate DeAraugo, Junie Morosi, Lyndsey Rodrigues, Sophie Masson and Irina Dunn.
Other communities are found in Indonesia, with significant populations living in Lamno (the so-called "mata biru" or blue-eyed people), Aceh, Maluku Islands and Kampung Tugu.
[422][423][424][425] In recent years many Indonesians of Portuguese descent have been active in the entertainment industry such as Puteri Indonesia Elfin Pertiwi Rappa or actress Millane Fernandez [id].
[430] Notable Thai of Portuguese descent include Francis Chit, Maria Guyomar de Pinha, Kung Nang Pattamasuta [th], Krystal Vee, and Neon Issara [th].
Portuguese contributions to the scientific world included the Caravel – a light and fast ship designed for coastal navigation and the Portolan – a maritime map used from the early Middle Ages.
[clarification needed][583] João Faras named the Southern Cross while Francisco de Pina, in Asia invented the modern Vietnamese alphabet (Quốc ngữ).
[598] Other companies include Sumol + Compal (drinks); Renova (tissue); Vista Alegre (ceramics); Nelo (MAR Kayaks Ltda) (boats); GestiFute (public relations); Pestana Group (tourism and leisure) and Salvador Caetano.
Portuguese farmers grow pears, apples, plums, cherries, olives, citrus fruits and grain crops such as wheat, rye, corn, oats, and vegetables such as legumes.
High seafood (fish, crustaceans including lobster, crab, shrimp, prawns, and octopus) consumption is supported by rich fisheries along Portugal's 1,800 km of coastline (1,115 miles).
Portugal has 19 named wine regions Denominação de Origem Controlada: Alenquer, Arruda, Bairrada, Beira Interior, Bucelas, Carcavelos, Colares, Dão, Douro, Encostas d'Aire, Lagoa, Lagos, Óbidos, Palmela, Portimão, Setúbal, Tavira, Távora-Varosa, and Torres Vedras.
Other Portuguese architects include Diogo de Arruda (chapter house window at the Convent of Christ, in Tomar), Pedro Nunes Tinoco and Filippo Terzi (Monastery of São Vicente de Fora), André Soares (Falperra Church), José António Caldas (dark room pioneer in Brazil), Carlos Amarante (Bom Jesus do Monte), João Luís Carrilho da Graça, José da Costa e Silva (established Neoclassical architecture in Portugal and Brazil), José Luis Monteiro, João Abel Manta, Huguet and Mateus Fernandes (Monastery of Batalha) Portuguese architects who made contributions abroad include Alfredo Azancot in Chile, Emanuele Rodriguez Dos Santos in Italy, and Jo Palma in Canada.
Besides fado, the country produced other popular music, including Portuguese Pop Rock, developed in the 1980s and 1990s by artists such as Xutos & Pontapés, Rui Veloso, and the Madredeus.
[613][614] Many Portuguese telenovelas have reached international audiences, such as A Única Mulher, Floribella, Morangos com Açúcar, Laços de Sangue and Conta-me como foi.