Portuguese vocabulary
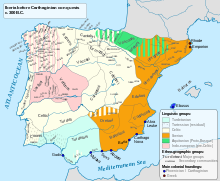
[1] Traces of the languages from native peoples of western Iberia (Gallaeci, Lusitanians, Celtici or Conii) persist in Portuguese, as shown below.
[11] The Celtic substratum is often overlooked,[12] due to the strong Latinisation of Celtic-derived[13] words in Portuguese and the ancient linguistic threads of pre-Roman origin.
[citation needed] Their vocabulary in Portuguese is often related to warfare/military topics, animals texugo (badger), natural world orvalho (dew), Human qualities like franqueza (frankness, candour), orgulho (pride), some verbs like ganhar (to gain), town and placenames such as Aldão,[145] Alderete, Albergaria-a-Velha, Albergaria-a-Nova (from Gothic 'haribergo'), Ermesinde and Esposende, where sinde and sende for instance; are derived from the Germanic "sinths" (military expedition), numerous Suebi[146] derivations like, Freamunde (from 'Fredemundus'), Vermunde, Amonde (Onomondi), Samonde, Gimonde, Aldão,[citation needed] Guadramil, Gondomil, Samil, Gosende, Guilhofrei (from Geodefredis), Esmoriz, Esmeriz (toponymics of Hermeric, king of the Suebians), Alhariz (toponymic of Aliaricus), Oriz, Touriz, Roriz, Gavieira, Gondoriz, Gondizalves, Gondar, Gondomar (from Gundomarus), Gondarém, Gudim, Guimarães (from Vimara), Torres Vedras (from Turres Veteras, 'old tower'[147]), Sousa, Terras de Sousa and Terras de Bouro (land of the Buri), Serra do Bouro, Bouro, are found mainly in the Minho (Braga) and Douro (Porto) regions- these two provinces present the highest concentration of Germanic toponyms in the Iberian Peninsula, as they historically correspond to old the Suebic Kingdom in the middle-ages.
It is very difficult to establish how the Suebi and Visigoth dialects differed from each other during that period, how much linguistic assimilation occurred, and therefore almost impossible to classify words with etymological certainty.
This article deals with Germanic personal names recorded and used in northern Portugal, Galicia and its adjoining regions: territories of the kingdom of the Suebi during the early Middle Ages from its 409 settlement to the 12th century.
Ideo que euenit in portione de filios Gunterodis, id est: Argiuitus, Gentibus, Tratiuigia, Recedrudi, Gaudiosus, Tequelo, Iulia, filios Stanildi, Sitiuidis, Gluscudilum, Framildi, Ruderigus, Sonobrida, Sabarigis, Argeleuba, Ostosia, Guntedrudia, Uitiza et Leuba, Guntildi, Iulia, Ragesindus, Sanildi cum sua filia Ermegundia, Seniorina, Uisteuerga, Sisulfus, Branderigus, Astruildi (...)" Germanic names were the most common personal names in Portugal-Galicia (Gallaecia) during the early and high Middle Ages, surpassing Christian and Roman names in number and popularity.
[201] The following names, used by the Suevi of Gallaecia during the fifth and sixth centuries, were recorded in chronicles, inscriptions and acts of local ecclesiastical councils: Hermericus, Heremigarius, Rechila, Rechiarius, Agriulfum, Maldras, Massila, Framta, Frumarius, Rechimundus, Remismundus, Veremundus, Chararici, Ariamirus, Ildericus, Theudomirus, Miro, Nitigisius, Uittimer, Anila, Remisol, Adoric, Eboricus, Siseguntia f, Audeca, Malaricus, Pantardus, Neufila, Hildemirus, Commundus, Ermaricus, Sunila, Becilla, Gardingus, Argiovitus, Gomedei, Rodomiro, Ermengontia f, Remisiwera f, Thuresmuda f, Suinthiliuba f. Many of the names, used by kings such as Miro, Reckila and Theudemirus, were used for local toponyms: Mirón,[202] Requián, Requiás, Requiás and Receá,[203] Tuimil and Toimil.
Many are related to war, victory, fame, boldness, strength and warlike qualities (bald-, funs-, hild-, gund-, nand-, rod-, seg-, send-), totemic animals (ar-, wulf-, ber-, ebur-) and weapons (brand-, bruni-, rand-, saru-); many others refer to knowledge, love and other peaceful qualities (fred-, leob-, mun-, ragi-, rad-, uin-).
Another group refers to the tribe, nation or country (conia-, fulc-, teod-, leod-, man-, truct-, gavi-, gogi-, kend-), and another appears to refer to Huns (Hun-), Suevi (Sav-), Goths (Gut-), Vandals (Vandal-), Celts (Vala-), Vendians/Slavs (Venet-), Galindians/Balths (Galind-), Franks (Frank-), Saxons (Sax-), Angles (Engl-), Danes (Dan-) and other peoples.
Although some elements are identical to others found in Celtic anthroponymy (And-, Dag-, -mar, -riks), others appear to be adaptations of Latin words and names incorporated in the Danube region: Florens, Fortis, Crescens.
XXI of his "Dicionário Etimológico da Língua Portuguesa": Several thousand such toponyms are known in northern and central Portugal, Galicia, western Asturias and other territories which were part of the Suebi kingdom.