Protein crystallization
[7] In 1909, the physiologist Edward T. Reichert, together with the mineralogist Amos P. Brown, published a treatise on the preparation, physiology and geometrical characterization of haemoglobin crystals from several hundreds animals, including extinct species such as the Tasmanian wolf.
Prior to Bernal and Hodgkin, protein crystallography had only been performed in dry conditions with inconsistent and unreliable results.
[8] In 1958, the structure of myoglobin (a red protein containing heme), determined by X-ray crystallography, was first reported by John Kendrew.
[4] Now, based on the protein crystals, the structures of them play a significant role in biochemistry and translational medicine.
However, crystallization of some proteins under ambient conditions would both decrease the entropy (negative ∆S) and increase the total energy (positive ∆H) of the system, and thus does not occur spontaneously.
[3] The nucleation step is critical for crystal formation since it is the first-order phase transition of samples moving from having a high degree of freedom to obtaining an ordered state (aqueous to solid).
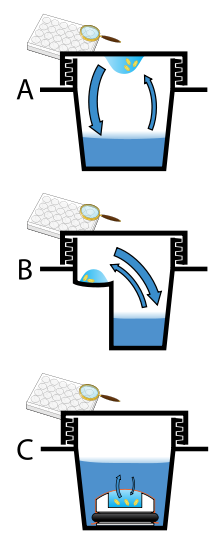
Hanging-drop apparatus involve a drop of protein solution placed on an inverted cover slip, which is then suspended above the reservoir.
The reason that oil is required is because such low volume of protein solution is used and therefore evaporation must be inhibited to carry out the experiment aqueously.
Microdialysis takes advantage of a semi-permeable membrane, across which small molecules and ions can pass, while proteins and large polymers cannot cross.
This technique brings together protein and precipitation solutions without premixing them, but instead, injecting them through either sides of a channel, allowing equilibrium through diffusion.
[3] These interactions depend on electron densities of molecules and the protein side chains that change as a function of pH.
[17] Smaller molecules crystallize better than macromolecules such as proteins, therefore, the use of chemical additives had been limited prior to the study by McPherson.
[17] High through-put methods exist to help streamline the large number of experiments required to explore the various conditions that are necessary for successful crystal growth.
There are numerous commercial kits available for order which apply preassembled ingredients in systems guaranteed to produce successful crystallization.
What would otherwise be slow and potentially error-prone process carried out by a human can be accomplished efficiently and accurately with an automated system.
Robotic crystallization systems use the same components described above, but carry out each step of the procedure quickly and with a large number of replicates.
[20] Frequently, problematic cysteine residues can be replaced by alanine to avoid disulfide-mediated aggregation, and residues such as lysine, glutamate, and glutamine can be changed to alanine to reduce intrinsic protein flexibility, which can hinder crystallization.. Macromolecular structures can be determined from protein crystal using a variety of methods, including X-ray diffraction/X-ray crystallography, cryogenic electron microscopy (CryoEM) (including electron crystallography and microcrystal electron diffraction (MicroED)), small-angle X-ray scattering, and neutron diffraction.