Quebec
By the European explorations of the 1500s, there were eleven Indigenous peoples: the Inuit and ten First Nations – the Abenakis, Algonquins (or Anichinabés), Atikamekw, Cree, Huron-Wyandot, Maliseet, Miꞌkmaqs, Iroquois, Innu and Naskapis.
[26] In 1603, Samuel de Champlain travelled to the Saint Lawrence River and, on Pointe Saint-Mathieu, established a defence pact with the Innu, Maliseet and Micmacs, that would be "a decisive factor in the maintenance of a French colonial enterprise in America despite an enormous numerical disadvantage vis-à-vis the British".
[31][32] The Compagnie des Cent-Associés, which had been granted a royal mandate to manage New France in 1627, introduced the Custom of Paris and the seigneurial system, and forbade settlement by anyone other than Catholics.
In 1713, following the Peace of Utrecht, the Duke of Orléans ceded Acadia and Plaisance Bay to Great Britain, but retained Île Saint-Jean, and Île-Royale where the Fortress of Louisbourg was subsequently erected.
When the British recognized the independence of the rebel colonies at the signing of the Treaty of Paris of 1783, it conceded Illinois and the Ohio Valley to the newly formed United States and denoted the 45th parallel as its border, drastically reducing Quebec's size.
Governor Haldimand drew Loyalists away from Quebec City and Montreal by offering free land on the north shore of Lake Ontario to anyone willing to swear allegiance to George III.
Events such as the North-West Rebellion, the Manitoba Schools Question and Ontario's Regulation 17 turned the promotion and defence of the rights of French Canadians into an important concern.
[75] Under the aegis of the Catholic Church and the political action of Henri Bourassa, symbols of national pride were developed, like the Flag of Carillon, and "O Canada" – a patriotic song composed for Saint-Jean-Baptiste Day.
Many organizations went on to consecrate the affirmation of the French-Canadian people, including the caisses populaires Desjardins in 1900, the Club de hockey Canadien in 1909, Le Devoir in 1910, the Congress on the French language in Canada in 1912, and L'Action nationale in 1917.
After enormous difficulty in the federal government, because almost every French-speaking MP opposed conscription while almost all English-speaking MPs supported it, the Military Service Act became law on August 29, 1917.
In an attempt to remedy this, the Quebec government enacted infrastructure projects, campaigns to colonize distant regions, financial assistance to farmers, and the secours directs – the ancestor to Canada's Employment Insurance.
[87] However, as early as 1948, French Canadian society began to develop new ideologies and desires in response to societal changes such as the television, the baby boom, workers' conflicts, electrification of the countryside, emergence of a middle class, the rural exodus and urbanization, expansion of universities and bureaucracies, creation of motorways, renaissance of literature and poetry, and others.
The Quiet Revolution was a period of modernization, secularization and social reform, where French Canadians expressed their concern and dissatisfaction with their inferior socioeconomic position, and the cultural assimilation of francophone minorities in the English-majority provinces.
[91] The Quiet Revolution was particularly characterized by the 1962 Liberal Party's slogan "Masters in our own house", which, to the Anglo-American conglomerates that dominated the economy and natural resources, announced a collective will for freedom of the French-Canadian people.
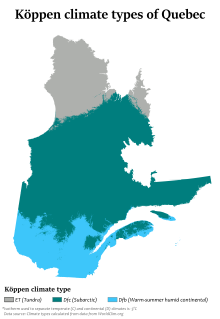
[137] Winters are long, very cold, and snowy, and among the coldest in eastern Canada, while summers are warm but very short due to the higher latitude and the greater influence of Arctic air masses.
Sea and semi-aquatic birds seen in Quebec are mostly the Canada goose, the double-crested cormorant, the northern gannet, the European herring gull, the great blue heron, the sandhill crane, the Atlantic puffin and the common loon.
The Société des établissements de plein air du Québec (SEPAQ) is the main body responsible for the management of national parks and wildlife reserves.
[173] Faced with the problem of expanding urban sprawl, agricultural zones were created to ensure the protection of fertile land, which make up 2% of Quebec's total area.
[270] Many aerospace companies are active here, including CMC Electronics, Bombardier, Pratt & Whitney Canada, Héroux-Devtek, Rolls-Royce, General Electric, Bell Textron, L3Harris, Safran, SONACA, CAE Inc., and Airbus, among others.
The Digital Alliance, which claims 191 active members in video games, online education, mobility and Internet services, estimates the annual revenue of the sector at $827 million in 2014.
[295] William Osler, Wilder Penfield, Donald Hebb, Brenda Milner, and others made significant discoveries in medicine, neuroscience and psychology while working at McGill University in Montreal.
In April 2012, plans were unveiled for the construction of an 800 km (497 mi) railway running north from Sept-Îles, to support mining and other resource extraction in the Labrador Trough.
The Quebec health system is also public, which means that the government acts as the main insurer and administrator, that funding is provided by general taxation, and that patients have access to care regardless of their income level.
The Prix du Québec is an award given by the government to confer the highest distinction and honour to individuals demonstrating exceptional achievement in their respective cultural field.
Quebec's most popular artists of the last century include the singers Félix Leclerc, Gilles Vigneault, Kate and Anna McGarrigle and Céline Dion.
[333][334] Les Rendez-vous du cinéma québécois is a festival surrounding the ceremony of the Jutra Awards Night that rewards work and personalities of Quebec cinema.
Many Quebec poets and prominent authors marked their era and today remain anchored in the collective imagination, like, among others, Philippe Aubert de Gaspé, Octave Crémazie, Honoré Beaugrand, Émile Nelligan, Lionel Groulx, Gabrielle Roy, Hubert Aquin, Michel Tremblay, Marie Laberge, Fred Pellerin and Gaston Miron.
The development of Quebec masterpieces in painting, printmaking and sculpture is marked by the contribution of artists such as Louis-Philippe Hébert, Cornelius Krieghoff, Alfred Laliberté, Marc-Aurèle Fortin, Marc-Aurèle de Foy Suzor-Coté, Jean Paul Lemieux, Clarence Gagnon, Adrien Dufresne, Alfred Pellan, Jean-Philippe Dallaire, Charles Daudelin, Arthur Villeneuve, Jean-Paul Riopelle, Paul-Émile Borduas and Marcelle Ferron.
Quebec has hosted several major sporting events, including the 1976 Summer Olympics, the Fencing World Championships in 1967, track cycling in 1974, and the Transat Québec-Saint-Malo race created in 1984.
The northeastern Franco-Ontarians of today, who live in Timmins, Hearst, Moosonee and Sault Sainte Marie, among others, are the descendants of emigrants from Quebec who worked in the mines of the area.



















|
Linguistic map of the province of Quebec (source: Statistics Canada, 2006 census)
Francophone majority, less than 33% Anglophone
Francophone majority, more than 33% Anglophone
Anglophone majority, more than 33% Francophone
Anglophone majority, less than 33% Francophone
Data not available
|
















