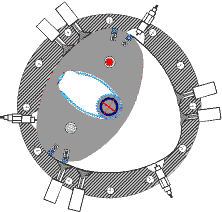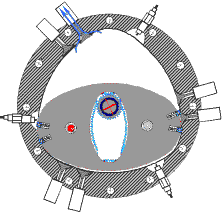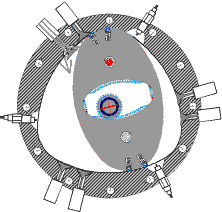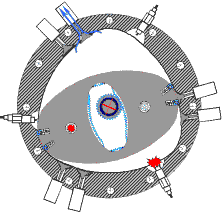
RKM engine
For instance: Hydraulics, fluid and gas transport systems, presses, fuel injection, irrigation, heating systems, hydraulic lifts, water jet engines, hydro- and pneumatic engines, and medical pumps.
All versions of the RKM incorporate a working chamber formed by smoothly conjugated circular arcs.
Hence, generally speaking, the trajectories of their centers of curvature are also non-analytical and, within the RKMs' geometry, have to have singular points.
Those corners, which represent singular points of the power shaft's trajectory, cannot be avoided or rounded to provide for the kinematically closed functioning of the gear.
The axis of rotation in the Wankel engine moves in a circle while that of the RKM is fixed (in the single power shaft version, temporarily with two possible positions).
In the RKM motor, the ignition takes place in a compact recess, while the Wankel's is in the work chamber itself.