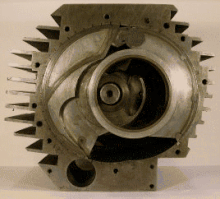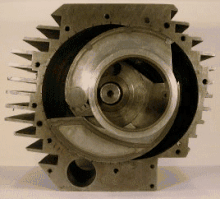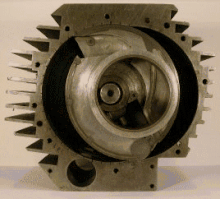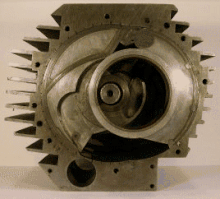
Pistonless rotary engine
Designs vary widely but typically involve one or more rotors, sometimes called rotary pistons.
Although many different designs have been constructed, only the Wankel engine has achieved widespread adoption.
However, both continue to be called rotary engines and only the context determines which type is meant, whereas the "pistonless" prefix is less ambiguous.
A pistonless rotary engine replaces the linear reciprocating motion of a piston with more complex compression/expansion motions with the objective of improving some aspect of the engine's operation, such as: higher efficiency thermodynamic cycles, lower mechanical stress, lower vibration, higher compression, or less mechanical complexity.
As of 2006[update] the Wankel engine is the only successful pistonless rotary engine, but many similar concepts have been proposed and are under various stages of development.