RNA-induced silencing complex
[5] This was only a couple of years after the discovery of RNA interference in 1998 by Andrew Fire and Craig Mello, who shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
[3] Hannon and his colleagues attempted to identify the RNAi mechanisms involved in gene silencing, by dsRNAs, in Drosophila cells.
Their results led Hannon and his colleagues to suggest RNAi degrades target mRNA through a 'sequence-specific nuclease activity'.
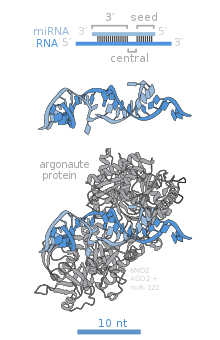
The RNase III Dicer is a critical member of RISC that initiates the RNA interference process by producing double-stranded siRNA or single-stranded miRNA.
Enzymatic cleavage of dsRNA within the cell produces the short siRNA fragments of 21-23 nucleotides in length with a two-nucleotide 3' overhang.
[8][9][10][11] The newly generated miRNA or siRNA act as single-stranded guide sequences for RISC to target mRNA for degradation.
The endonucleolytic cleavage of the mRNA complementary to the RISC's guide strand by Argonaute protein is the key to RNAi initiation.
RISC can modulate the loading of ribosome and accessory factors in translation to repress expression of the bound mRNA transcript.
It has been suggested this mechanism acts as a 'self-reinforcing feedback loop' as the degraded nascent transcripts are used by RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) to generate more siRNAs.
[26] In Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Arabidopsis, the processing of dsRNA targets into siRNA by Dicer RNases can initiate a gene silencing pathway by heterochromatin formation.
[27] The siRNA generated by RISCs seem to have a role in degrading DNA during somatic macronucleus development in ciliates of the genus Tetrahymena.
[28] Ago, Argonaute; Dcr, Dicer; Dmp68, D. melanogaster orthologue of mammalian p68 RNA unwindase; eIF2C1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2C1; eIF2C2, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2C2; Fmr1/Fxr, D. melanogaster orthologue of the fragile-X mental retardation protein; miRNP, miRNA-protein complex; NR, not reported; Tsn, Tudor-staphylococcal nuclease; Vig, vasa intronic gene.
[40] The RISC-loading complex (RLC) is the essential structure required to load dsRNA fragments into RISC in order to target mRNA.
[48] Ago, Argonaute; Dcr, Dicer; Dmp68, D. melanogaster orthologue of mammalian p68 RNA unwindase; eIF2C1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2C1; eIF2C2, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2C2; Fmr1/Fxr, D. melanogaster orthologue of the fragile-X mental retardation protein; Tsn, Tudor-staphylococcal nuclease; Vig, vasa intronic gene.