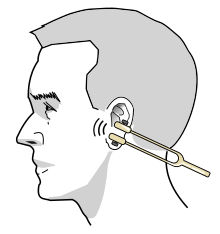
Rinne test
The Rinne test (/ˈrɪnə/ RIN-ə) is used primarily to evaluate loss of hearing in one ear.
Once the patient signals they can't hear it, the still vibrating tuning fork is then placed 1–2 cm from the auditory canal.
Note that the words positive and negative are used in a somewhat confusing fashion here, as compared to their typical use in medical tests.
Therefore, some prefer to avoid using the terms "positive" or "negative", and simply state if the test was normal or abnormal.
In such a case, the Weber test will, however, show signs of lateralization, implying some kind of pathology.