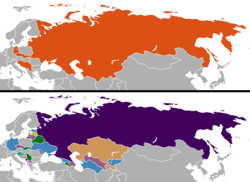
Territorial evolution of Russia
While Western Europe colonized the New World, the Tsardom of Russia expanded overland – principally to the east, north and south.
[5] According to Kazakh scholar Kereihan Amanzholov, Russian colonialism had "no essential difference with the colonialist policies of Britain, France, and other European powers".
[18] In February 1924, Tahanrih and Shakhtinsky counties (okruhas) were transferred from the Donetsk Governorate of Ukraine to Russia's North Caucasus krai.
[19][20] By the end of World War II the Soviet Union had annexed: Of these, Pechenga, Salla, Tuva, Kaliningrad Oblast, the Kurils, and Sakhalin were added to the territory of the RSFSR.
After Russian defeat at the Battle of Grozny, the First Chechen War ended with Russia recognizing the new Ichkerian government of president Maskhadov in January 1997 and signing a peace treaty in May.
A few weeks later, an armed conflict broke out the Donbas region of Ukraine, in which the Kremlin denies an active role, but is widely considered to be fuelled by soldiers, militants, weapons, and ammunition from the Russian Federation.
On February 21, 2022, the Russian president Putin signed a decree recognizing the independence of two Donbas republics in Ukraine, and invaded the region.
After failing to seize Ukraine's capital Kyiv for over a month, the Russian defence minister stated that the main goal of the war was the "liberation of the Donbas",[27] but later a Russian general stated that it was to seize eastern and southern Ukraine right through to Transnistria, a breakaway territory in Moldova.
[28][29] On 30 September 2022, Putin announced in a speech[30] that Russia was to annex four partially occupied regions of Ukraine: Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk, and Zaporizhzhia Oblasts.