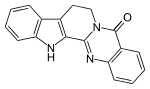
Rutecarpine
Rutecarpine or rutaecarpine is a COX-2 inhibitor isolated from Tetradium ruticarpum, a tree native to China.
[2] In contrast to synthetic COX-2 inhibitors like etoricoxib and celecoxib, rutecarpine does not appear to cause negative effects on the cardiovascular system.
[3] Microsome studies suggest that rutaecarpine may be at least a weak inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4 enzymes.
[6] Rutecarpine metabolism is complex and proceeds along several routes, primarily involving the addition of a single hydroxyl group by CYP3A4.
[7] Rutecarpine has been shown to decrease the overall bioavailability of caffeine in rats by up to 80 percent,[8] likely through induction of enzymes CYP1A2 and CYP2E1.