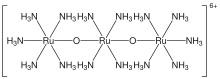
Ruthenium red
Ruthenium red (RR) has also been used as a pharmacological tool to study specific cellular mechanisms.
[1] These include mammalian ion channels (CatSper1, TASK, RyR1, RyR2, RyR3, TRPM6, TRPM8, TRPV1, TRPV2, TRPV3, TRPV4, TRPV5, TRPV6, TRPA1, mCa1, mCa2, CALHM1[2][3]) TRPP3,[4] a plant ion channel, Ca2+-ATPase, mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter,[5] tubulin, myosin light-chain phosphatase, and Ca2+ binding proteins such as calmodulin.
Ruthenium red displays nanomolar potency against several of its binding partners (e.g. TRPV4, ryanodine receptors,...).
For example, it is a potent inhibitor of intracellular calcium release by ryanodine receptors (Kd ~20 nM).
[6] As a TRPA1 blocker, it assists in reducing the airway inflammation caused by pepper spray.