SCIAMACHY
SCIAMACHY (SCanning Imaging Absorption SpectroMeter for Atmospheric CHartographY; Greek: σκιαμαχεί: analogously: "Fighting shadows") was one of ten instruments aboard of ESA's ENVIronmental SATellite, ENVISAT.
[2] SCIAMACHY, aboard the ENVISAT satellite, was launched by ESA (European Space Agency) from Kourou, French Guiana, in March 2002.
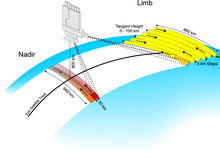
The absorption, reflection and scattering characteristics of the atmosphere were determined by measuring the extraterrestrial solar irradiance and the upwelling radiance observed in different viewing geometries.
The ratio of extraterrestrial irradiance and the upwelling radiance can be inverted to provide information about the amounts and distribution of important atmospheric constituents, which absorb or scatter light, and the spectral reflectance (or albedo) of the Earth's surface.
SCIAMACHY was conceived to improve global knowledge and understanding of a variety of issues of importance for the chemistry and physics of the Earth's atmosphere (troposphere, stratosphere and mesosphere) and potential changes resulting from either anthropogenic behavior or natural phenomena.