Shunzhi Emperor
In the 1650s, he faced a resurgence of Ming loyalist resistance, but by 1661 his armies had defeated the Qing's last enemies, Koxinga and the Prince of Gui, both of whom would succumb the following year.
[8] His string of victories ended in February 1626 at the siege of Ningyuan, where Ming commander Yuan Chonghuan defeated him with the help of recently acquired Portuguese cannon.
[21] On 17 February 1644, Jirgalang, who was a capable military leader but looked uninterested in managing state affairs, willingly yielded control of all official matters to Dorgon.
On 24 April of that year, rebel leader Li Zicheng breached the walls of the Ming capital, pushing the Chongzhen Emperor to hang himself on a hill behind the Forbidden City.
[26] Hearing the news, Dorgon's Chinese advisors Hong Chengchou and Fan Wencheng (范文程; 1597–1666) urged the Manchu prince to seize this opportunity to present themselves as avengers of the fallen Ming and to claim the Mandate of Heaven for the Qing.
[30] Aided by Wu Sangui's elite soldiers, who fought the rebel army for hours before Dorgon finally chose to intervene with his cavalry, the Qing won a decisive victory against Li Zicheng at the Battle of Shanhai Pass on 27 May.
[44] In June 1645, Dorgon eventually decreed that all official documents should refer to him as "Imperial Uncle Prince Regent" (Huang shufu shezheng wang 皇叔父攝政王), which left him one step short of claiming the throne for himself.
"[47] Despite tax remissions and large-scale building programs designed to facilitate the transition, in 1648 many Chinese civilians still lived among the newly arrived Banner population and there was still animosity between the two groups.
"[51] Under the Shunzhi Emperor's reign, the average number of graduates per session of the metropolitan examination was the highest of the Qing dynasty ("to win more Chinese support"), until 1660 when lower quotas were established.
[56] Under the pressure of Qing armies, Li was forced to leave Xi'an in February 1645, and he was killed—either by his own hand or by a peasant group that had organized for self-defense in this time of rampant banditry—in September 1645 after fleeing though several provinces.
[67] On 21 July 1645, after Jiangnan had been superficially pacified, Dorgon issued a most inopportune edict ordering all Chinese men to shave their forehead and to braid the rest of their hair into a queue identical to those of the Manchus.
When the city wall was finally breached on 9 October 1645, the Qing army led by Ming defector Liu Liangzuo (劉良佐; d. 1667) massacred the entire population, killing between 74,000 and 100,000 people.
[80] The two Ming regimes fought each other until 20 January 1647, when a small Qing force led by Li Chengdong captured Guangzhou, killed the Shaowu Emperor, and sent the Yongli court fleeing to Nanning in Guangxi.
[84] Meanwhile, in October 1646, Qing armies led by Hooge (the son of Hong Taiji who had lost the succession struggle of 1643) reached Sichuan, where their mission was to destroy the kingdom of bandit leader Zhang Xianzhong.
[107] The scandal, which soon spread to Nanjing examination circles, uncovered the corruption and influence-peddling that was rife in the bureaucracy, and that many moralistic officials from the north attributed to the existence of southern literary clubs and to the decline of classical scholarship.
[108] During his short reign, the Shunzhi Emperor encouraged Han Chinese to participate in government activities and revived many Chinese-style institutions that had been either abolished or marginalized during Dorgon's regency.
He discussed history, classics, and politics with grand academicians such as Chen Mingxia (see previous section) and surrounded himself with new men such as Wang Xi (王熙; 1628–1703), a young northern Chinese who was fluent in Manchu.
[112] Eunuchs had been kept under tight control during Dorgon's regency, but the young emperor used them to counter the influence of other power centers such as his mother the Empress Dowager and former regent Jirgalang.
[120] Also in 1646 sultan Abu al-Muhammad Haiji Khan, a Moghul prince who ruled Turfan, had sent an embassy requesting the resumption of trade with China, which had been interrupted by the fall of the Ming dynasty.
[124] In 1651 the young emperor invited to Beijing the Fifth Dalai Lama, the leader of the Yellow Hat Sect of Tibetan Buddhism, who, with the military help of Khoshot Mongol Gushri Khan, had recently unified religious and secular rule in Tibet.
[127] To prepare for the arrival of this "living Buddha," the Shunzhi Emperor ordered the building of the White Dagoba (baita 白塔) on an island on one of the imperial lakes northwest of the Forbidden City, at the former site of Qubilai Khan's palace.
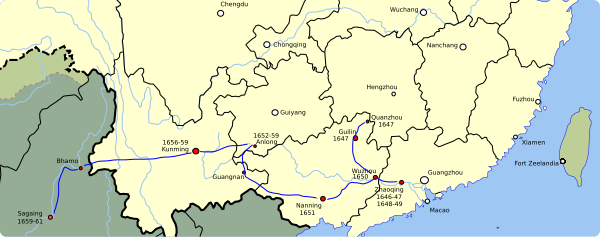
In early August 1652, Li Dingguo, who had served as general in Sichuan under bandit king Zhang Xianzhong (d. 1647) and was now protecting the Yongli Emperor of the Southern Ming, retook Guilin (Guangxi province) from the Qing.
[135] Headquartered in Changsha (in what is now Hunan province), he patiently built up his forces; only in late 1658 did well-fed and well-supplied Qing troops mount a multipronged campaign to take Guizhou and Yunnan.
[135] In late January 1659, a Qing army led by Manchu prince Doni took the capital of Yunnan, sending the Yongli Emperor fleeing into nearby Burma, which was then ruled by King Pindale Min of the Toungoo dynasty.
[137] In 1659, just as the Shunzhi Emperor was preparing to hold a special examination to celebrate the glories of his reign and the success of the southwestern campaigns, Zheng sailed up the Yangtze River with a well-armed fleet, took several cities from Qing hands, and went so far as to threaten Nanjing.
[d] The emperor's will expressed his regret about his Chinese-style ruling (his reliance on eunuchs and his favoritism toward Chinese officials), his neglect of Manchu nobles and traditions, and his headstrong devotion to his consort rather than to his mother.
[173] The regents also adopted aggressive policies toward the Qing's Chinese subjects: they executed dozens of people and punished thousands of others in the wealthy Jiangnan region for literary dissent and tax arrears, and forced the coastal population of southeast China to move inland in order to starve the Taiwan-based Kingdom of Tungning run by descendants of Koxinga.
[178] Once victory had become certain, a special examination for "eminent scholars of broad learning" (Boxue hongru 博學鴻儒) was held in 1679 to attract Chinese literati who had refused to serve the new dynasty.
"[181] Ironically, however, the prolonged Pax Manchurica that followed the Kangxi consolidation made the Qing unprepared to face aggressive European powers with modern weaponry in the nineteenth century.
[186] Empress Consort Concubine Enthroned in 1626 as Khan, Hong Taiji changed the dynastic name to "Great Qing" in 1636 and claimed the title of emperor.In 1644, the Shunzhi Emperor began to rule over China proper, replacing the Ming dynasty.