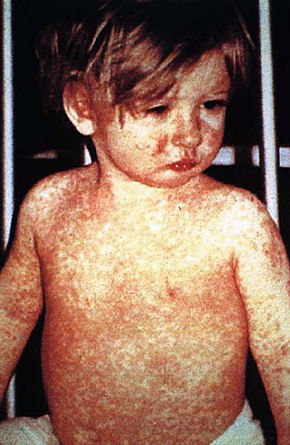
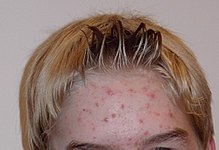
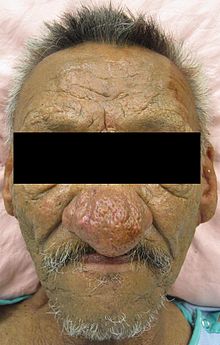
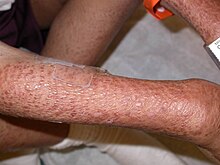
List of skin conditions
[2] The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue.
[8][11] The function of blood vessels within the dermis is fourfold: to supply nutrition, to regulate temperature, to modulate inflammation, and to participate in wound healing.
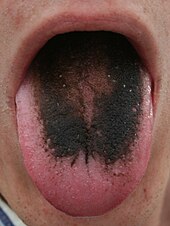
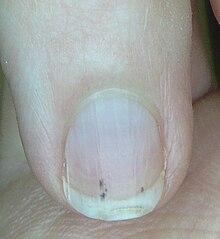
[14] Conditions of the human integumentary system constitute a broad spectrum of diseases, also known as dermatoses, as well as many nonpathologic states (like, in certain circumstances, melanonychia and racquet nails).
[19][20] Clinically, the diagnosis of any particular skin condition is made by gathering pertinent information regarding the presenting skin lesion(s), including the location (such as arms, head, legs), symptoms (pruritus, pain), duration (acute or chronic), arrangement (solitary, generalized, annular, linear), morphology (macules, papules, vesicles), and color (red, blue, brown, black, white, yellow).
[21] Diagnosis of many conditions often also requires a skin biopsy which yields histologic information[22][23] that can be correlated with the clinical presentation and any laboratory data.
[36][37][38][39] Cutaneous congenital anomalies are a diverse group of disorders that result from faulty morphogenesis, the biological process that forms the shape of a human body.
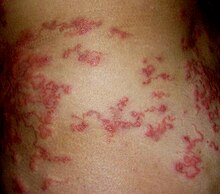
[35][40][41] Connective tissue diseases are caused by a complex array of autoimmune responses that target or affect collagen or ground substance.
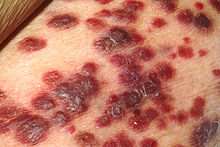
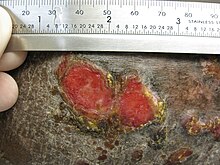
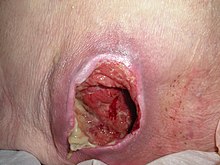
[26][69] Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions often have distinct morphologic characteristics that may be an indication of a generalized systemic process or simply an isolated superficial infection.
[69][71] Mycosis-related cutaneous conditions are caused by fungi or yeasts, and may present as either a superficial or deep infection of the skin, hair, or nails.
[69] Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites in humans are caused by several groups of organisms belonging to the following phyla: Annelida, Arthropoda, Bryozoa, Chordata, Cnidaria, Cyanobacteria, Echinodermata, Nemathelminthes, Platyhelminthes, and Protozoa.
[69][73] Lichenoid eruptions are dermatoses related to the unique, common inflammatory disorder lichen planus, which affects the skin, mucous membranes, nails, and hair.
[80][81][82] Monocyte- and macrophage-related cutaneous conditions are characterized histologically by infiltration of the skin by monocyte or macrophage cells,[10] often divided into several categories, including granulomatous disease,[83] histiocytoses,[84] and sarcoidosis.
[95][96] Psoriasis is a common, chronic, and recurrent inflammatory disease of the skin characterized by circumscribed, erythematous, dry, scaling plaques.
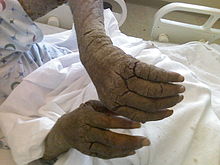
[34] Skin conditions resulting from errors in metabolism are caused by enzymatic defects that lead to an accumulation or deficiency of various cellular components, including, but not limited to, amino acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
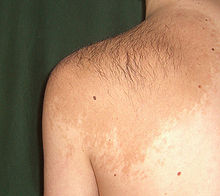
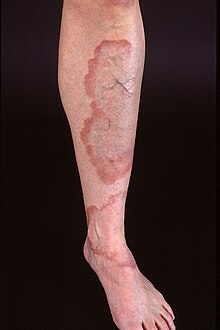
[16] Skin conditions resulting from physical factors occur from a number of causes, including, but not limited to, hot and cold temperatures, friction, and moisture.
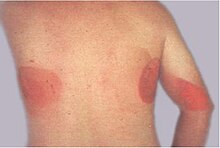
[105] Angioedema, which can occur alone or with urticaria, is characterized by a well-defined, edematous swelling that involves subcutaneous tissues, abdominal organs, or upper airway.