Slewing drive
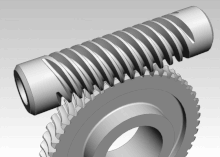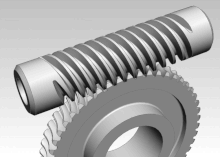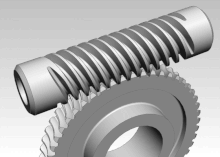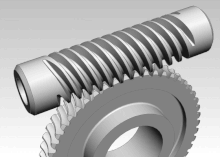
The slewing drive is a gearbox that can safely hold radial and axial loads without brakes, as well as transmit a torque for rotating.
Slewing drives are made by manufacturing gearing, bearings, seals, housing, motor and other auxiliary components and assembling them into a finished gearbox.
Pappus of Alexandria (3rd century AD), a Greek mathematician, is credited with an early version of the endless screw, which would later evolve into the worm drive.
[1] Many slewing drive concepts found prominence with the emergence of larger scale construction and engineering in the height of the Greek and Roman Empires.
According to an extensive series of tests by the Hamilton Gear & Machine Co., chill-cast nickel-phosphor bronze ranked first in resistance to wear and deformation.