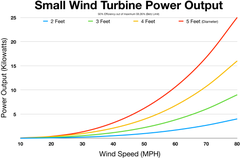
Small wind turbine
[5] Although natural fibers are susceptible to quality variations, high moisture uptake and low thermal stability that make them undesirable for larger blades, small turbines can still take advantage of them.
[8] Nepal has used small blade turbines made of coated timber including Sal, Saur, Sisau, Uttish, Tuni, Okhar, pine, and lakuri wood.
[9] Beyond wood, bamboo-based composites may also be used in both large and small wind turbines due to their low density and carbon sequestration ability—which makes bamboo materials environmentally friendly.
Dynamic braking is a technique used to regulate the speed of a turbine by discharging excess energy through a resistive load during high winds to prevent damage.
The controller, activated when batteries reach a certain voltage, turns on the load using a solenoid or solid-state relay, the latter of which has the added benefit of "failing open".
The country is aiming to increase renewable energy investment in part as a response to the Fukushima radiation crisis in March 2011.
[20] The feed-in tariff applies to solar panels and small wind turbines and requires utilities to buy back electricity generated from renewable energy sources at government-established rates.
[21] Properties in rural or suburban parts of the UK can opt for a wind turbine with inverter to supplement local grid power.
The UK's Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS) provides feed-in tariffs to owners of qualified small wind turbines.
In 2011 IEA Wind published a Recommended Practice, which describes the tests and procedures required to apply the label.
[28] Croatia is an ideal market for small wind turbines due to Mediterranean climate and numerous islands with no access to the electric grid.
In contrast, small photovoltaic systems in Germany benefited from a high feed-in tariff, at times above 50 Euro-Cent per kilowatt hour.
For the operation of a small wind turbine with a capacity below 50 kilowatt the tariff amounts to 8.5 Euro-Cent for a period of 20 years.
[38] Organizations such as Practical Action have designed DIY wind turbines that can be easily built by communities in developing nations and are supplying concrete documents on how to do so.
[39][40] Designs of DIY small wind turbines date back to the early 1970s, and were further developed by the back-to-the-land movement of the late 1970s in the United States and Europe.