Variable renewable energy
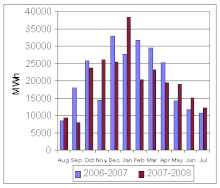
[5]: 55 The penetration of intermittent renewables in most power grids is low: global electricity generation in 2021 was 7% wind and 4% solar.
[7] These, along with renewables typically being asynchronous generators, provide a challenge to grid operators, who must make sure supply and demand are matched.
Although wind power forecasts have been used operationally for decades, as of 2019[update] the IEA is organizing international collaboration to further improve their accuracy.
[19] Wind-generated power is a variable resource, and the amount of electricity produced at any given point in time by a given plant will depend on wind speeds, air density, and turbine characteristics, among other factors.
Solar output varies throughout the day and through the seasons, and is affected by dust, fog, cloud cover, frost or snow.
Many of the seasonal factors are fairly predictable, and some solar thermal systems make use of heat storage to produce grid power for a full day.
Thermal energy storage systems like the small Spanish Gemasolar Thermosolar Plant can improve the match between solar supply and local consumption.
[50] Alternatives to burning coal and natural gas which produce fewer greenhouse gases may eventually make fossil fuels a stranded asset that is left in the ground.
Highly integrated grids favor flexibility and performance over cost, resulting in more plants that operate for fewer hours and lower capacity factors.
The introduction of large amounts of highly variable power generation may require changes to existing procedures and additional investments.
[52] Additionally, the storage of energy to fill the shortfall intermittency or for emergencies can be part of a reliable power supply.
The ability to quickly replace lost generation, typically within timescales of 30 seconds to 30 minutes, is termed "spinning reserve".
Hydroelectric facilities with storage capacity, such as the traditional dam configuration, may be operated as base load or peaking plants.
In France large users such as CERN cut power usage as required by the System Operator - EDF under the encouragement of the EJP tariff.
[55][56] Energy demand management refers to incentives to adjust use of electricity, such as higher rates during peak hours.
[57] Some loads such as desalination plants, electric boilers and industrial refrigeration units, are able to store their output (water and heat).
Most large systems also have a category of loads which instantly disconnect when there is a generation shortage, under some mutually beneficial contract.
Such mechanisms can include: Pumped storage hydropower is the most prevalent existing technology used, and can substantially improve the economics of wind power.
Along with substantial durability which allows them to be cycled frequently without noticeable life reduction, they also have very fast response and ramp rates.
[75] Multiple wind farms spread over a wide geographic area and gridded together produce power more constantly and with less variability than smaller installations.
The ability to predict wind output is expected to increase over time as data is collected, especially from newer facilities.
[82] The International Energy Agency says that sector coupling is needed to compensate for the mismatch between seasonal demand and supply.
[83] Electric vehicles can be charged during periods of low demand and high production, and in some places send power back from the vehicle-to-grid.
[84][85] Penetration refers to the proportion of a primary energy (PE) source in an electric power system, expressed as a percentage.
Discussion of acceptable or unacceptable penetration figures should be treated and used with caution, as the relevance or significance will be highly dependent on local factors, grid structure and management, and existing generation capacity.
Many types of generation, particularly fossil fuel derived, will have cost externalities such as pollution, greenhouse gas emission, and habitat destruction, which are generally not directly accounted for.
The magnitude of the economic impacts is debated and will vary by location, but is expected to rise with higher penetration levels.
By accepting the lowest bid the government commits to buy at that price per kWh for a fixed number of years, or up to a certain total amount of power.
With smart meters, private consomers can also be motivated i.e. to load an electric car when enough renewable energy is available and prices are cheap.