Son of Sevenless
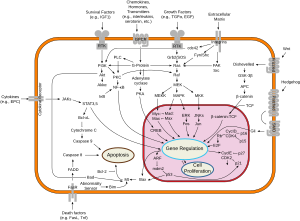
In cell signalling, Son of Sevenless (SOS) refers to a set of genes encoding guanine nucleotide exchange factors that act on the Ras subfamily of small GTPases.
[1] When sevenless is mutated or otherwise dysfunctional during development of the fly's ultraviolet light-sensitive compound eye, the seventh, central photoreceptor (R7) of each ommatidium fails to form.
Ras-GTPases act as molecular switches that bind to downstream effectors, such as the protein kinase c-Raf, and localise them to the membrane, resulting in their activation.
[6] A common feature of these genes is that their products have all been strongly implicated as positive regulators of the Ras/MAP kinase signal transduction pathway.
This may be explained because the SOS1 protein adopts an auto-inhibited conformation dependent on multiple domain-to-domain interactions that cooperate to block access of the SOS1 catalytic core to its Ras-GTPase targets.