MAPK/ERK pathway
[3] Activated SOS then promotes the removal of GDP from a member of the Ras subfamily (most notably H-Ras or K-Ras).
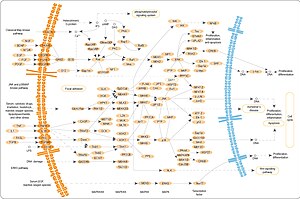
The ERK pathway plays an important role of integrating external signals from the presence of mitogens such as epidermal growth factor (EGF) into signaling events promoting cell growth and proliferation in many mammalian cell types.
The restriction point (R-point) marks the critical event when a mammalian cell commits to proliferation and becomes independent of growth stimulation.
Although the R-point has been linked to various activities involved in the regulation of G1–S transition of the mammalian cell cycle, the underlying mechanism remains unclear.
Using single-cell measurements, Yao et al., shows that the Rb–E2F pathway functions as a bistable switch to convert graded serum inputs into all-or-none E2F responses.
[8] Growth and mitogen signals are transmitted downstream of the ERK pathway are incorporated into multiple positive feedback loops to generate a bistable switch at the level of E2F activation.
The first is a result of mitogen stimulation though the ERK leading to the expression of the transcription factor Myc, which is a direct activator of E2F.
Finally, these interactions are all reinforced by an additional positive feedback loop by E2F on itself, as its own expression leads to production of the active complex of Cyclin E and CDK2, which further serves to lock in a cell's decision to enter S-phase.
[8] The EGFR-ERK/MAPK (epidermal growth factor receptor extracellular-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase) pathway stimulated by EGF is critical for cellular proliferation, but the temporal separation between signal and response obscures the signal-response relationship in previous research.In 2013, Albeck et al.[9] provided key experimental evidence to fill this gap of knowledge.
Single cell imaging experiments have shown ERK to be activated in stochastic bursts in the presence of EGF.
Furthermore, the pathway has been shown to encode the strength of signaling inputs though frequency modulated pulses of its activity.
They found that longer periods of ERK activity stimulate S phase entry, as suggested by increased pulse length.
Two inhibitors yield actually a little bit different result: gefitinib, at intermediate concentration, would induce pulsatory behavior and also bimodal shift, which is not observed with PD.
To understand how the integrated ERK pathway output (which should be independent of either frequency or amplitude) affect the proliferation rate, they used the combination of a wide range of EGF and PD concentrations and find that there’s actually an inverted “L” shape single curvilinear relationship, which suggests that at low levels of ERK pathway output, small changes in signal intensity correspond to large changes in proliferative rate, while large changes in signal intensity near the high end of the dynamic range have little impact on proliferation.
These results illustrate a form of encoded molecular memory though the history of mitogen signaling through ERK and stress response though p53.
Many compounds can inhibit steps in the MAP/ERK pathway, and therefore are potential drugs for treating cancer,[14][15][16][17][18] such as Hodgkin disease.
[18] Some MEK inhibitors include cobimetinib, CI-1040, PD0325901, binimetinib (MEK162), selumetinib,[18] and trametinib (GSK1120212)[20] It has been found that acupoint-moxibustion has a role in relieving alcohol-induced gastric mucosal injury in a mouse model, which may be closely associated with its effects in up-regulating activities of the epidermal growth factor/ERK signal transduction pathway.
[22] The developmental syndromes caused by germline mutations in genes that alter the RAS components of the MAP/ERK signal transduction pathway are called RASopathies.