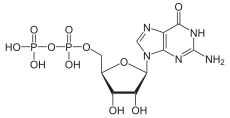
Guanosine diphosphate
The hydrolysis of GTP to GDP is facilitated by GTPase enzymes, which utilize a conserved active site motif known as the GTPase-activating protein (GAP).
The water molecule attacks the γ-phosphate of GTP, leading to the formation of a pentavalent transition state.
[2] GDP is involved in intracellular signaling processes functioning as a critical regulator in the activity of GTPases.
The interconversion between GDP and GTP is tightly controlled and serves as a molecular timer for signal transduction pathways.
The hydrolysis of GTP to GDP by the GTPase activity of the G-protein restoring the inactive state, thus terminates the signaling event.