Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe
The Ersparungsclasse der Allgemeinen Versorgungsanstalt, established in Hamburg in 1778, is widely viewed as the first modern savings bank.
[8]: 564 In 1921, further legislative changes enabled them to underwrite and sell securities more broadly, thus allowing them to act practically as universal banks.
The savings banks in East Germany were nationalized and separated from the rest of the network in 1945, but reintegrated into it after German reunification in 1990.
The Träger position (German: Trägerschaft) cannot be sold, and it does not grant rights to the Sparkasse's financial surplus, which is typically retained or used for local public welfare projects.
[9]: 14 Until the early 21st century, the Träger also provided explicit financial guarantees to the institutions they controlled, but these guarantees were mostly phased out under an agreement concluded on 17 July 2001 between a group of German negotiators and the European Commission represented by Competition Commissioner Mario Monti, known in German as the Brüsseler Konkordanz [de].
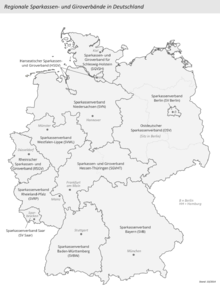
The Regional Principle (German: Regionalprinzip [de]) stipulates that entities of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe such as Sparkassen or public insurers have a local monopoly within the group within the geographical area in which they are established, namely the territory of their Träger.
The states of Hesse and Schleswig-Holstein have less restrictive legislation on the Regional Principle than the other German Länder, linked to the fact that, as in Hamburg, they have Sparkassen under the legal-form of joint-stock companies (Aktiengesellschaft) as opposed to public-sector entities.
[11] It operates as an umbrella organization to facilitate decision-making processes, coordinate strategy, and represent its members' political and regulatory interests at the national and international levels.
[15] Each savings bank is independent, locally managed and concentrates its business activities on customers in the territory in which it is situated under the Regional Principle.
[20] Although independent and regionally spread, the savings banks act as one unit under the brand Sparkasse with its iconic logo and recognizable red hue.
[22] After multiple mergers and restructurings, five Landesbanken operated in Germany as of late 2022: FIDES Alpha and Gamma are trustee entities for the regional sub-funds of the Sparkassenverbände within the Institutional Protection Scheme (IPS) under the DSGV, and FIDES Beta and Delta are trustees for the sub-fund of the Landesbanken in the IPS.
[26][27] Landesbank Berlin (LBB) does not belong in the same category as it was converted into a joint-stock company (German: Aktiengesellschaft) in 2007, when the DSGV rescued it and took full ownership through two of its legal entities, Erwerbsgesellschaft der S-Finanzgruppe mbH & Co. KG (owning 89.37 percent) and Beteiligungsgesellschaft der S-Finanzgruppe mbH & Co. KG (owning 10,63 percent).
The nine public insurers that belong to the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe are:[29] The core business of the eight Landesbausparkassen [de] ("Land-level building savings banks") is collective real estate saving products (Bausparen) and low-interest residential mortgage loans,[30] with a share of the German mortgage market of about one-third and cumulative assets of €74.5 billion.[10]: 59 .
[citation needed] DekaBank with its subsidiaries is the central asset manager of the German Savings Bank Finance Group.
[10]: 66 The internal legal and financial arrangements of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe are complex, in line with its largely decentralized structure that mirrors its long history.
The core feature of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe is a set of mutual support arrangements known as an Institutional Protection Scheme (IPS) in EU law, namely the Capital Requirements Regulation.
[4] As of 2021, the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe IPS included 13 participating sub-funds (German: Teilfonds): The Landesbanks' sub-fund includes the six remaining such institutions (BayernLB, Helaba, LBBW, NORD/LB, SaarLB, and Landesbank Berlin AG) as well as the national DekaBank; the Berlin entities Landesbank Berlin Holding and Berlin Hyp; the defunct WestLB's "bad bank", Portigon AG; Frankfurter Bankgesellschaft, the group's main private bank; Weberbank [de], another private bank once owned by WestLB and subsequentlty by the Potsdam-based Mittelbrandenburgische Sparkasse [de]; and two specialized arms of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe, S-Kreditpartner [de] (car loans and consumer credit) and S Broker [de] (securities brokerage).
[9]: 19 The exact formula for such equalization, however, has not been made clear in the public domain, and the protection is in no way automatic but instead relies on voting within the Sparkassenverbände and other managers of the relevant sub-funds.
[38]: 18 The corresponding uncertainty has generated concerns from the supervisors at the European Central Bank and BaFin and partial reform of the IPS adopted by the DSGV in August 2021.
[9]: 23–24 A new national protection fund is to be set up with 2.6 billion euro to be paid in by the Sparkassen and Landesbanken between 2025 and 2032, which is expected to allow for faster intervention in future cases of need, complementing the existing IPS setup of 13 regional and sectoral sub-funds.
[38]: 18 A revision of the IPS statutes (German: Satzung) in early 2024 led credit rating agency Moody's to upgrade its ratings of IPS members and specifically of the Landesbanks, noting: "The revised statutes result in a more rule-based IPS that implements an early intervention system with clearly identified triggers and timely escalation of decision-making steps as well as increased ex-ante funds over time, which, in the view of the rating agency, increase the likelihood and timeliness of support".
[10]: 77–79 in August 2021, the DSGV members unanimously adopted a resolution to reform the system and establish a Deposit Insurance Fund, gradually from 2024-2025.