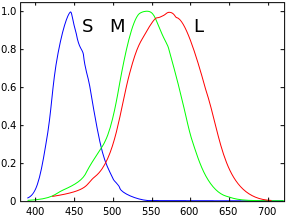
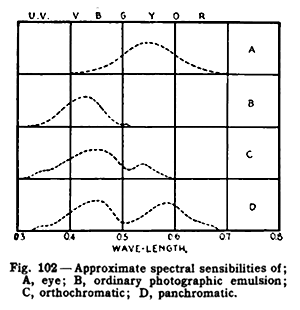
Spectral sensitivity
[5] A database of camera spectral sensitivity is created and its space analyzed.
[7] In sensor systems, where the output is easily quantified, the responsivity can be extended to be wavelength dependent, incorporating the spectral sensitivity.
[8] When a system's responsivity is a fixed monotonic nonlinear function, that nonlinearity can be estimated and corrected for, to determine the spectral sensitivity from spectral input–output data via standard linear methods.
[10] In spite of these complexities, however, the conversion of light energy spectra to the effective stimulus, the excitation of the photopigment, is quite linear, and linear characterizations such as spectral sensitivity are therefore quite useful in describing many properties of color vision.
[12] In other contexts, the spectral sensitivity is expressed as the relative response per light energy, rather than per quantum, normalized to a peak value of 1, and a quantum efficiency is used to calibrate the sensitivity at that peak wavelength.