Student debt
As of 2018[update], Canada is ranked third in the world (behind Russia and South Korea) for the percentage of people ages 25–34 who have completed tertiary education.
[2] To assist low-income citizens with student debt, Canada's Interest Relief program offers a six-month reprieve from mandatory payments for up to a total of 30 months, during which the government covers interest, preventing the loan amount from increasing further.
[7] In 2014, a Chilean activist, artist Francisco Tapia, known as "Papas Fritas" (French Fries), "Burned $500 million worth of debt papers" from Viña del Mar University and displayed the ashes in a van as an art project.
These grants are generally used for housing and compensate for up to 80% of rent for students who live independently and are not qualified to receive child benefits.
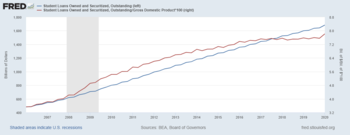
[26] According to economist Sebastian Burnside, student debt is the fastest-growing type of borrowing and is rapidly becoming economically significant.
It is argued that the artwork addresses the subject matter of the materialism of money and brings to light the political issues of the U.K student loan system.
Several scholars attribute the student debt crisis to the influence of neoliberal policies and practices, which have bolstered tuition costs while simultaneously reducing state funding for higher education.
[38] During the Reagan presidency student debt increased, and following the Great Recession climbed significantly as states slashed public funding for higher education.
[41] A report by the Brookings Institution warned that the student loan default rate could reach nearly 40 percent by 2023.
[42] In 2019, Theresa Sweet and other student loan debtors filed a claim against the United States Department of Education, arguing that they had been defrauded by their colleges.
[46] The Economist reported in June 2014 that U.S. student loan debt exceeded $1.2 trillion with over 7 million debtors in default.
"[50] Student loan borrowers that attended a for-profit and two-year community colleges earn low annual salaries, an average of $22,000 for people withdrawing from schools as of 2010.
[51] In January 2019, the Federal Reserve said that student loan debt has more than doubled in the last decade, and is forcing many in the millennial generation to delay buying homes.
[53] Beth Akers, a senior fellow at the Manhattan Institute for Policy Research, points out that 66% of millennials have no college debt; most of whom do have debt proportional to their income; and that for those who drop out or fail to get a high-income job after getting an expensive degree, there are government programs that limit payments to a reasonable percentage of income and that forgive loans after 10–20 years if they cannot be repaid.
[55] There have been significant efforts made via social media for the Occupy Student Debt campaign.
[56] While some success stories of students eliminating debt have been reported,[57] they are met with heavy skepticism.
[55] Because of this, other organizations, such as Rebuild the Dream, Education Trust, and the Young Invincible, have joined in the effort and started similar platforms.
[62] HR 4170 also includes the “10-10” programs, which allow borrowers to pay 10% of their discretionary income for ten years with the remaining balance forgiven afterwards.
[63] The severity of the student debt burden represents such a threat to the middle class that some have demanded a general bailout.
The demonstrations took place just days after fast food workers went on strike for a minimum wage of $15 an hour and union rights.
[67] A February 2018 research paper from the Levy Economics Institute of Bard College argues that government cancellation student debt in the United States would result in rising consumer demand, along with economic growth and increased employment.
Senator from Vermont Bernie Sanders, who was also seeking the 2020 Democratic nomination, offered a plan for the cancellation of all 1.8 trillion in outstanding student loan debt which would be paid for with a tax on Wall Street speculation.
[70] According to a Hill-HarrisX poll, 58% of registered voters are in favor of making public colleges tuition free and also support abolishing all outstanding student loan debt.
The Head of Army Recruiting Command, Maj. Gen. Frank Muth, said that "One of the national crises right now is student loans, so $31,000 is [about] the average.
[73] These effects include feelings of anxiety, nervousness, and tension, as well as difficulty sleeping and worry about criticism from peers.
[76] In April 2024, the Biden administration initiated the forgiveness of $7.4 billion in student loan debt for 277,000 borrowers, as part of its broader strategy to address the issue.
This action added to the $153 billion already forgiven for nearly 4.3 million individuals, reflecting the administration's ongoing efforts in tackling student loan debt.