Sustainable food system
Further, it is humane and just, protecting farmers and other workers, consumers, and communitiesThe European Union's Scientific Advice Mechanism defines a sustainable food system as a system that:[16] provides and promotes safe, nutritious and healthy food of low environmental impact for all current and future EU citizens in a manner that itself also protects and restores the natural environment and its ecosystem services, is robust and resilient, economically dynamic, just and fair, and socially acceptable and inclusive.
It does so without compromising the availability of nutritious and healthy food for people living outside the EU, nor impairing their natural environmentIndustrial agriculture causes environmental impacts, as well as health problems associated with both obesity and hunger.
[35] Industrial agriculture replaces human labor using increased usage of fossil fuels, fertilizers, pesticides, and machinery and is heavily reliant on monoculture.
This expectation places the onus on individuals to voluntarily and often without external incentives, expend effort to educate themselves about sustainable behaviours and specific product choices.
Subsequently, consumers are urged to alter their decision-making patterns concerning production and consumption, driven by prioritised ethical values and sometimes health benefits, even when significant drawbacks are prevalent.
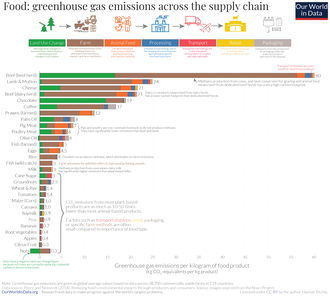
[49][50][51] Agricultural pollution refers to biotic and abiotic byproducts of farming practices that result in contamination or degradation of the environment and surrounding ecosystems, and/or cause injury to humans and their economic interests.
One example is the growing body of research indicating that properly formulated and balanced vegan diets can meet the nutritional needs of dogs and cats without compromising their health.
This is significant from a sustainability perspective as traditional pet food production heavily relies on animal-based ingredients, which contribute to deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and overfishing.
Additionally, sustainable pet food may also prioritize the use of responsibly sourced ingredients, organic farming practices, and minimal packaging waste.
[95] A 2022 review concluded that "low and moderate meat consumption levels are compatible with the climate targets and broader sustainable development, even for 10 billion people".
[77] In June 2023, the European Commission's Scientific Advice Mechanism published a review of all available evidence and accompanying policy recommendations to promote sustainable food consumption and reducing meat intake.
[102][103][104] The principal mitigation strategies identified for reduction of agricultural nitrous oxide emissions are avoiding over-application of nitrogen fertilizers and adopting suitable manure management practices.
[107] Methane belching from cattle might be reduced by intensification of farming,[108] selective breeding,[109] immunization against the many methanogens,[109] rumen defaunation (killing the bacteria-killing protozoa),[110] diet modification (e.g. seaweed fortification),[111] decreased antibiotic use,[112] and grazing management.
[113] Measures that increase state revenues from meat consumption/production could enable the use of these funds for related research and development and "to cushion social hardships among low-income consumers".
[115] "Policy sequencing" to gradually extend regulations once established to other forest risk commodities (e.g. other than beef) and regions while coordinating with other importing countries could prevent ineffectiveness.
[123][124] Important mitigation options for reducing the greenhouse gas emissions from livestock include genetic selection,[125][126] introduction of methanotrophic bacteria into the rumen,[127][128] vaccines, feeds,[129] toilet-training,[130] diet modification and grazing management.
[137] However, consulting firm Sustainalytics assured that these companies are not more sustainable than meat-processors competitors such as food processor JBS, and they don't disclose all the CO2 emissions of their supply chain.
[170] In 2019, though global production of calories kept pace with population growth, there are still more than 820 million people who have insufficient food and many more consume low-quality diets leading to micronutrient deficiencies.
One factor includes growth of large-scale producing and selling units in bulk to chain stores which displays merchandising power from large scale market organizations as well as their mergence with manufactures.
[172] Another main factor involves protecting public interest, which means better adaptation for product and service, resulting in rapid development of food distribution.
[172] An additional factor comprises new changes and forms of newly invented technical processes such as developments of freezing food, discovered through experiments, to help with distribution efficiency.
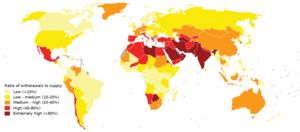
[181] Likewise, effects of climate change on agriculture can result in lower crop yields and nutritional quality due to for example drought, heat waves and flooding as well as increases in water scarcity,[182][183] pests and plant diseases.
Individual studies have named several proposed options of such[190][191][144] and the restricted website Project Drawdown has aggregated and preliminarily evaluated some of these measures.
Money is another big factor that determines how long the process will take and who is working, and it is treated differently in low income countries' food systems.
A portfolio of coordinated strategies is called for to address this challenge.In January 2020, the EU put improvements to the food system at the core of the European Green Deal.
That will require a mix of incentives, information and binding policies governing all aspects of food production and distribution.During 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference, 45 countries pledged to give more than 4 billion dollars for transition to sustainable agriculture.
STBs are hubs often created in rural areas with significant rates of small-scale farming that combine knowledge of traditional practices with new innovations and technology implementation.
The program was ultimately proven to be successful, and the study found that the merging of traditional practices and appropriate technology was instrumental in higher crop yields.
[236] In collaboration with the Food and Land Use Coalition (FOLU), CEEW (council for energy, environment and water), has given an overview of the current state of sustainable agriculture practices and systems (SAPSs) in India.
Further proposals for several measures for promoting SAPSs, including restructured government support and rigorous evidence generation for benefits and implementation of sustainable farming are ongoing progress in Indian Agriculture.