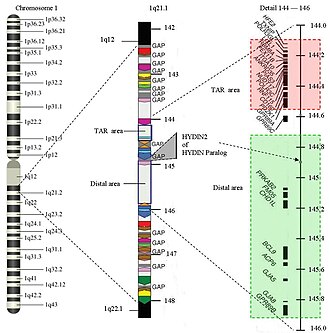
TAR syndrome
TAR syndrome (thrombocytopenia with absent radius) is a rare genetic disorder that is characterized by the absence of the radius bone in the forearm and a dramatically reduced platelet count.
[5][6] Treatments range from platelet transfusions[1] to surgery aimed at either centralizing the hand over the ulna to improve functionality of the hand or aimed at 'normalizing' the appearance of the arm, which is much shorter and 'clubbed'.
The infant mortality rate has been curbed by new technology, including platelet transfusions, which can even be performed in utero[citation needed].
For most people with TAR, platelet counts improve as they grow out of childhood.
[7] 40 years later Hall collected 40 cases and introduced the name "Thrombocytopenia with absent radius".