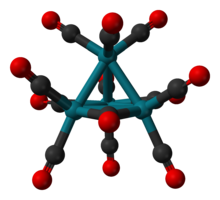
Tetracobalt dodecacarbonyl
It is a black crystalline compound that is insoluble in water and easily oxidized by air.
The molecule consists of a tetrahedral Co4 core, but the molecular symmetry is C3v.
[2][3] Rh4(CO)12 adopts the same C3v structure but Ir4(CO)12 has perfect Td symmetry with no bridging CO ligands groups.
[4] The Rh4 and Ir4 clusters are more thermally robust than that of the Co4 compound, reflecting the usual trend in the strengths of metal-metal bond for second and third row metals vs those for the first row metals.
There has been disagreement between the theoretically predicted and experimental structure of tetracobalt dodecacarbonyl.