Tetrandrine
[1] It is isolated from the plant Stephania tetrandra,[2] and other Chinese and Japanese herbs.
[5][6][7] Tetrandrine has potential therapeutic value to prevent excess scarring/fibrosis in conjunctiva following trabeculectomy or in patients with severe conjunctival inflammation.
[8] Tetrandrine has anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrogenic actions, which make tetrandrine and related compounds potentially useful in the treatment of lung silicosis, liver cirrhosis, and rheumatoid arthritis.
[9] Tetrandrine has also been shown to inhibit entry of Ebola virus into host cells in vitro and showed therapeutic efficacy against Ebola in preliminary studies on mice.
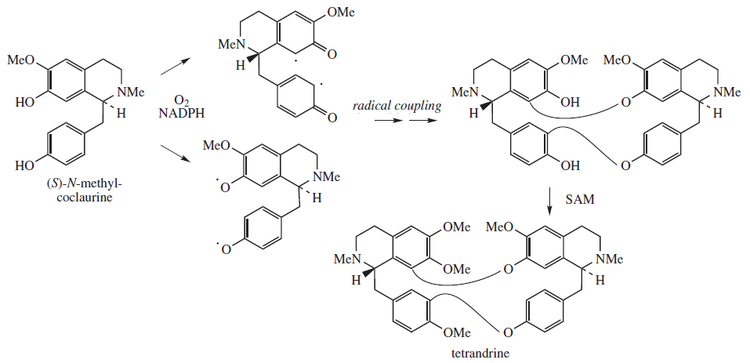
[11][12][13] Tetrandrine is biosynthesized from a free radical coupled dimerization of S-N-methylcoclaurine:[14] Synonyms include fanchinine, hanfangchin A, NSC 77037, (S,S)-(+)-tetrandrine, sinomenine A, TTD, tetrandrin, d-tetrandrine, and GW-201.