Car body configurations
The configuration of a car body is typically determined by the layout of the engine, passenger and luggage compartments, which can be shared or separately articulated.
A one-box design, also called a monospace, mono-box or monovolume configuration[1]—approximates in shape a single volume comprising engine, cabin and cargo areas, in part by locating the base of a vehicle's A-pillars further forward.
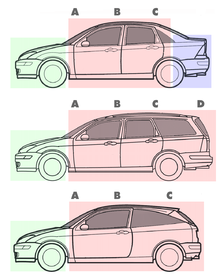
[1][2] Three-box design is a broad automotive styling term describing a coupé, sedan/saloon, notchback or hatchback where—when viewed in profile—principal volumes are articulated into three separate compartments or boxes: engine, passenger and cargo.
This style was later used by its larger Škoda Superb, which marketed as the TwinDoor, within the liftgate operable as a trunk lid or as a full hatchback.
[5][6] In 2018, the Wall Street Journal wrote: "from gangster getaway cars and the Batmobile to the humble family sedan, the basic three-box configuration of a passenger car—low engine compartment, higher cabin, low trunk in the rear—has endured for decades as the standard shape of the automobile.
Other, predominantly European manufacturers followed suit, with the most recent generation of Opel Astra may no longer to be offered as the four-door notchback.