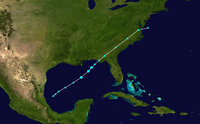
Timeline of the 2019 Atlantic hurricane season
These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most tropical systems form.
While Lorenzo did not affect land as a Category 5 hurricane, it caused US$367 million in damage and killed 19, with over half of the deaths being attributed to the sinking of a tugboat known as the Bourbon Rhode.
[5][6][7] In March 2021, the name Dorian was retired from reuse in the North Atlantic by the World Meteorological Organization.
[8] This timeline documents tropical cyclone formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, and dissipations during the season.
Additionally, figures for maximum sustained winds and position estimates are rounded to the nearest 5 units (knots, miles, or kilometers), following the convention used in the National Hurricane Center's products.