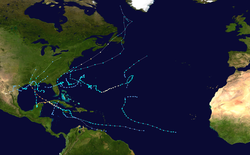
Tropical cyclones in 2002
The costliest and deadliest tropical cyclone of the year was Typhoon Rusa, killing 238 in South Korea and causing $4.2 billion (2002 USD) in damages.
The accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) index for the 2002 (seven basins combined), as calculated by Colorado State University was 812 units.
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is responsible for tropical cyclones in the North Atlantic and East Pacific.
Other, unofficial agencies that provide additional guidance in tropical cyclone monitoring include the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) and the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC).
This leads to the formation of a band of warm ocean water in the equatorial Eastern Pacific basin, marked by a reduction in upwelling.
[4] By contrast, the Eastern Pacific basin exhibits lower wind shear and higher sea surface temperatures, leading to more active cyclone seasons.
It ended early however, with no tropical storms forming after October 6—a rare occurrence caused partly by El Niño conditions.
Most destruction was due to Isidore, which caused about $1.28 billion (2002 USD) in damage and killed seven people in the Yucatán Peninsula and later the United States, and Hurricane Lili, which caused $1.16 billion (2002 USD) in damage and 15 deaths as it crossed the Caribbean Sea and eventually made landfall in Louisiana.
Hurricane Fausto had no effect on land, but it regenerated into a weak tropical storm at an abnormally high latitude.
[12] Nine storms developed in July, many of which influenced the monsoon trough over the Philippines to produce heavy rainfall and deadly flooding.
[17][nb 4] During this time, Tropical Storm Kammuri struck southern China with a large area of rainfall that damaged or destroyed 245,000 houses.
There were 153 deaths related to the storm, mostly inland in Hunan,[18] and damage totaled $322 million (¥2.665 billion CNY).
Two storms – Ele and Huko – entered the basin from the Central Pacific, east of the International Date Line.
[20] It went on to strengthen into a weak cyclonic storm, being designated ARB 01, and make landfall in Oman four days later, causing intense damage.
[20] BOB 05 formed very far south on December 21, scraped Sri Lanka, and dissipated in the open bay.
[34] Dianne passed close to the Cocos Islands, intensified into a Category 3 tropical cyclone, and moved westward into the South-West Indian Ocean on 11 April.
[35] On 26 May, Tropical Cyclone Upia, the season's last storm, formed near Papua New Guinea and was named by TCWC Port Moresby.
[38] The 2002 half of the season began with Tropical Storm Cyprien, which made landfall in western Madagascar and dissipated on 3 January.
[39]Two weeks later, Intense Tropical Cyclone Dina formed, causing record flooding in Mauritius and Reunion.
[38] Later in March, Tropical Cyclone Ikala developed in the south-central Indian Ocean, moving south and dissipating without affecting land.
[38] On 9 April, Tropical Cyclone Dianne crossed over from the Australian region and was renamed Jery, becoming extratropical two days later without affecting land.
The storm inflicted $50,000 damages on Seychelles, the most destruction caused by a tropical cyclone in 50 years, before dissipating on 8 September.
[46] Days later, Tropical Cyclone Boura formed, moving west and dissipating two weeks later without affecting land.
[47] In the Southern Hemisphere basins, January, at the height of the austral summer, is the most active month by cumulative number of storms since records began.
[38] The month saw a high number of tropical cyclones – eleven – although most failed to develop past depression intensity, with only four being named.
[42] The first storm to form in February, Cyclone Chris, would also become the strongest, with a pressure of 920 hPa (27.17 inHg), and deadliest, causing twelve deaths, of the month.
Mitag would intensify to become the first super typhoon ever in March,[54] eventually causing $150 million in damage to Micronesia.
[48][38] Meanwhile, in the Northern Hemisphere basins, sea surface temperatures are still far too low to normally support tropical cyclogenesis.
The exception is the Western Pacific, which usually sees its first storm, often a weak depression, at some point between January and April.
[38] The only other storm to affect land that month was Tropical Depression 03W, which made landfall in the Philippines, causing $2.4 million in damage and 35 deaths.