Diagnosis of tuberculosis
The medical history includes obtaining the symptoms of pulmonary TB: productive, prolonged cough of three or more weeks, chest pain, and hemoptysis.
The (Class) B notification program is an important screening strategy to identify new arrivals who have a high risk for TB.
[5] In patients incapable of producing a sputum sample, common alternative sample sources for diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis include gastric washings, laryngeal swab, bronchoscopy (with bronchoalveolar lavage, bronchial washings, and/or transbronchial biopsy), and fine needle aspiration (transtracheal or transbronchial).
NAA techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) are the basis of molecular diagnosis of TB.
The test simultaneously detects Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) and resistance to rifampin (RIF) in less than 2 hours.
New automated systems that are faster include the MB/BacT, BACTEC 9000, VersaTREK, and the Mycobacterial Growth Indicator Tube (MGIT).
[13] In active pulmonary TB, infiltrates or consolidations and/or cavities are often seen in the upper lungs with or without mediastinal or hilar lymphadenopathy or pleural effusions ( tuberculous pleurisy).
However, chest radiographs may be used to rule out the possibility of pulmonary TB in a person who has a positive reaction to the tuberculin skin test and no symptoms of the disease.
[citation needed] Cavitation or consolidation of the apexes of the upper lobes of the lung or the tree-in-bud sign[15] may be visible on an affected patient's chest X-ray.
[citation needed] Much less expensive than traditional X-Ray, MMR was quickly adopted and extensively utilized in some countries, in the 1950s.
[citation needed] The procedure went out of favor, as the incidence of tuberculosis dramatically decreased, but is still used in certain situations, such as the screening of prisoners and immigration applicants.
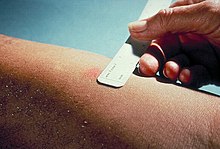
The Mantoux skin test is used in the United States and is endorsed by the American Thoracic Society and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The equivalent Mantoux test positive levels done with 10 TU (0.1 ml 100 TU/ml, 1:1000) are An induration (palpable raised hardened area of skin) of more than 5–15 mm (depending upon the person's risk factors) to 10 Mantoux units is considered a positive result, indicating TB infection.
[citation needed] The blood tests QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube and T-SPOT.TB use these antigens to detect people with tuberculosis.
[27] A 2012 study at Stanford University confirmed that addition of immune boosters can make the IGRA more reliable in terms of separating positive from negative individuals.
[28] A study from the University of Southampton shows that variations in environmental temperatures can have a profound effect on the performance of IGRA.
[32] In 2015, World Health Organization recommended the use of the Alere Determine TB LAM Ag assay for people with HIV and a CD4 count below 100 cells/μL and in those defined as seriously ill according to WHO criteria (respiratory rate >30 breaths per min, body temperature >39 °C, heart rate >120 beats per min, or unable to walk unaided).
[33] This recommendation was informed by a Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis of 12 cross-sectional or cohort studies that showed a relatively low pooled sensitivity of 45% and specificity of 92% against a microbiological reference standard.
[34] Despite the limited sensitivity, test-guided initiation of anti-TB treatment reduced mortality in immunocompromised, hospitalized PLHIV.
[37] Compared with the Alere Determine TB LAM Ag assay, the Fujifilm SILVAMP TB LAM assay includes novel monoclonal antibodies directed towards the 5-methylthio-d-xylofuranose (MTX) epitope and a silver amplification technology to enable higher diagnostic sensitivity at high specificity.
[42] In 2022, a study reported the use of a fingerstick blood point-of-care triage test by Cepheid (company) looking for messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of 3 genes in response to TB.
The Xpert MTB Host Response test calculated a polygenic risk score based on the expression levels of guanylate-binding protein 5 [GBP5], dual-specificity phosphatase 3 [DUSP3], and Krüppel-like factor 2 [KLF2] genes to differentiate between active TB and other diseases.
[43] In 2007, a systematic review of adenosine deaminase by the NHS Health Technology Assessment Programme concluded "There is no evidence to support the use of ADA tests for the diagnosis of pulmonary TB.
[46][47] In 2018, the international nonprofit organization APOPO was working with Sokoine University of Agriculture in Tanzania to train African giant pouched rats (Cricetomys ansorgei) to detect the "scent" of tuberculosis.
[48] A recent study shows that "rats increased pediatric tuberculosis detection by 67.6%" and that training these creatures could help address the current challenges related to the diagnosis of this illness in children.