United States Armed Forces
[21] The history of the U.S. Armed Forces dates back to 14 June 1775, with the creation of the Continental Army, even before the Declaration of Independence marked the establishment of the United States.
[67][68] As a special operations force, Army Rangers are generally better equipped than standard infantry, utilizing the FN SCAR rifle.
[77][78][79] The Air Defense Artillery is responsible for defending geopolitical assets and providing maneuver forces with the freedom to move on the battlefield by deterring the enemy and destroying aerial threats, missile attacks, and surveillance platforms.
The MIM-104 Patriot is capable of defeating a wide range of threats including aircraft, helicopters, UAVs, ballistic and cruise missiles, and Weapons of Mass Destruction.
[80] The Terminal High Altitude Area Defense protects strategic critical assets by conducting long-range endo-and-exo-atmospheric engagements of ballistic missiles using the world's largest air-transportable X-band radar.
[86] Major aircraft include the AH-64 Apache, which serves as the Army's attack helicopter, the UH-60 Black Hawk, and the CH-47 Chinook for troop and cargo transport.
[99] Marine Corps artillery operates the M777 howitzer and the M142 HIMARS, both supporting the ground combat element and the Navy at sea by striking enemy ships.
[102] Notably, the aviation combat element also includes Low-Altitude Air Defense Battalions, which employ the FIM-92 Stinger surface-to-air missile.
[115] The Naval Surface Forces operates eleven nuclear-powered aircraft carriers (CVN), split between the Nimitz-class and the newer Gerald R. Ford-class.
The Navy also operates a complement of smaller Freedom-class and Independence-class littoral combat ships (LCS) that can be modularly reconfigured for specific mission sets.
[122] Los Angeles-class, Seawolf-class, and Virginia-class nuclear-powered attack submarines are capable of performing sea control missions by destroying enemy submarines and surface ships, conducting surveillance and reconnaissance, performing irregular warfare, covert troop insertion, mine and anti-mine operations, and land attack missions with tomahawk cruise missiles.
These include the P-3C Orion and P-8A Poseidon, which conduct anti-submarine warfare operations and serve as maritime patrol aircraft, alongside the unmanned MQ-4C Triton.
The B-2A Spirit stealth bomber is capable of conducting both conventional and nuclear strike operations flying through air defenses.
[144] The B-52H Stratofortress is a long-range, heavy bomber that the Air Force has flown since the 1950s and operates a variety of conventional and nuclear munitions, including the AGM-86 air-launched cruise missile.
Global access teams assess and open airfields, ranging from international airports to dirt strips, in permissive or hostile locations to facilitate the landing and operation of air forces.
[192] The Space Force's GPS system has become an integral element of the global information infrastructure, being used in virtually all sectors of the economy, including agriculture, aviation, marine transportation, surveying and mapping, and transit navigation.
[223] The Future Vertical Lift program is intended to replace the current helicopter fleet flown by the Army Aviation Branch.
Other sub-efforts include developing a common operating environment, ensuring the network is interoperable with the other services and allied countries, and increasing the mobility and reducing the signature of its command posts.
[223] Finally, the Army is looking to improve the equipment of its soldiers in the Infantry Branch with the Next Generation Squad Weapon, the Integrated Visual Augmentation System, and the Synthetic Training Environment.
The Littoral Combat Team is organized around an infantry battalion with an anti-ship missile battery, focused on conducting sea denial operations in support of the Navy.
The Marine Corps is also looking to replace its UH-1Y Venom helicopters through the Future Vertical Lift program and is in the process of acquiring a significant number of unmanned aerial vehicles, such as the MQ-9 Reaper.
[231][230] With Naval Aviation, the service is continuing to procure additional Gerald R. Ford-class aircraft carriers and F-35C Lightning II stealth fighters.
It is also procuring the AGM-181 Long Range Stand Off Weapon to replace the AGM-86 ALCM as a nuclear air-launched cruise missile for the B-21 Raider and the B-52 Stratofortress.
The Deep Space Advanced Radar Capability (DARC) is intended to track objects in geosynchronous orbit with three sites, one in the United States, one in the Indo-Pacific, and one in Europe.
[237] The Navigation Technology Satellite-3 (NTS-3), building on the Space Force's Global Positioning System constellation, is an Air Force Research Laboratory spacecraft that will operate in geosynchronous orbit to test advanced techniques and technologies to detect and mitigate interference to positioning, navigation, and timing capabilities and increase system resiliency for military, civil, and commercial users.
[255]: 180–184 Beginning in 1965, efforts to increase the number of women in the armed forces accompanied concern about the expiration of the Selective Service Act and reduction in enlistment standards to ensure sufficient troops to support the Vietnam War.
[255]: 187–203 During the Vietnam War, 600 women served in the country as part of the Air Force, along with 500 members of the WAC and over 6,000 medical personnel and support staff.
[279] A study conducted by the RAND Corporation suggests that women who make the military their careers experience improved rates of promotion.
[286] This order is used for the display of service flags as well as the placement of soldiers, marines, sailors, airmen, guardians, and coast guardsmen in formations and parades.
The Navy did not officially recognize 13 October 1775 as its birth date until 1972, when then–chief of naval operations Admiral Elmo Zumwalt authorized it to be observed as such.

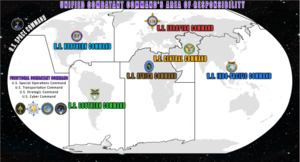











































Air Force and Space Force
Marine Corps
Navy
Army










