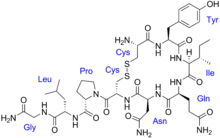
Vasopressin
It then travels down the axon terminating in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity (hyperosmolality).
First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons.
Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure.
Some AVP may be released directly into the brain from the hypothalamus, and may play an important role in social behavior, sexual motivation and pair bonding, and maternal responses to stress.
[13] A very similar substance, lysine vasopressin (LVP) or lypressin, has the same function in pigs and its synthetic version was used in human AVP deficiency, although it has been largely replaced by desmopressin.
Vasopressin stimulates sodium chloride reabsorption in the thick ascending limb of the nephron by activating signaling pathways.
Increased NKCC2 activity aids in water reabsorption in the collecting duct through aquaporin 2 channels by creating a hypo-osmotic filtrate.
[29] The AVP that is measured in peripheral blood is almost all derived from secretion from the posterior pituitary gland (except in cases of AVP-secreting tumours).
For example, AVP is also synthesized by parvocellular neurosecretory neurons of the PVN, transported and released at the median eminence, from which it travels through the hypophyseal portal system to the anterior pituitary, where it stimulates corticotropic cells synergistically with CRH to produce ACTH (by itself it is a weak secretagogue).
[49] The structure of oxytocin is very similar to that of the vasopressins: It is also a nonapeptide with a disulfide bridge and its amino acid sequence differs at only two positions.
Further, argipressins act on V1a, V1b, and V2 receptors which consequently lead to higher eGFR and lower vascular resistance in the lungs.
The most common side effects during treatment with vasopressin are dizziness, angina, chest pain, abdominal cramps, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, trembling, fever, water intoxication, pounding sensation in the head, diarrhoea, sweating, paleness, and flatulence.
[53] The use of lysine vasopressin is contraindicated in the presence of hypersensitivity to beef or pork proteins, increased BUN and chronic kidney failure.
It is recommended that it be cautiously used in instances of perioperative polyuria, sensitivity to the drug, asthma, seizures, heart failure, a comatose state, migraine headaches, and cardiovascular disease.
[53] Decreased AVP release (neurogenic — i.e. due to alcohol intoxication or tumour) or decreased renal sensitivity to AVP (nephrogenic, i.e. by mutation of V2 receptor or AQP) leads to diabetes insipidus, a condition featuring hypernatremia (increased blood sodium concentration), polyuria (excess urine production), and polydipsia (thirst).