X-ray detector
The contrast compounds have high atomic numbered elements in them that (like bone) essentially block the X-rays and hence the once hollow organ or vessel can be more readily seen.
Some elements chosen proved to be harmful – for example, thorium was once used as a contrast medium (Thorotrast) – which turned out to be toxic, causing a very high incidence of cancer decades after use.
[3] When the film is exposed to radiation the halide is ionised and free electrons are trapped in crystal defects (forming a latent image).
[12] The light given off during laser stimulation is collected by a photomultiplier tube, and the resulting signal is converted into a digital image by computer technology.
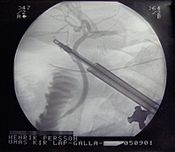
[13] X-rays are also used in "real-time" procedures such as angiography or contrast studies of the hollow organs (e.g. barium enema of the small or large intestine) using fluoroscopy.
Angioplasty, medical interventions of the arterial system, rely heavily on X-ray-sensitive contrast to identify potentially treatable lesions.
Unlike film or CR no manual scanning or development step is required to obtain a digital image, and so in this sense both systems are "direct".
Silicon drift detectors (SDDs), produced by conventional semiconductor fabrication, provide a cost-effective and high resolving power radiation measurement.
[21][22] Current applications include bone densitometry and SPECT but flat panel detectors suitable for radiographic imaging are not yet in production.
[24][25] Common semiconductor diodes, such as PIN photodiodes or a 1N4007, will produce a small amount of current in photovoltaic mode when placed in an X-ray beam.
This can provide sensitivity advantages over current (amorphous selenium) direct detectors, albeit with a potential trade-off in resolution.
[20] Indirect flat panel detectors (FPDs) are in widespread use today in medical, dental, veterinary, and industrial applications.
The TFT array consists of a sheet of glass covered with a thin layer of silicon that is in an amorphous or disordered state.
At a microscopic scale, the silicon has been imprinted with millions of transistors arranged in a highly ordered array, like the grid on a sheet of graph paper.
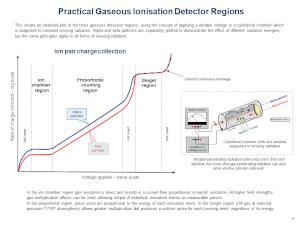
Since every electron cause an avalanche of approximately the same size the collected charge is proportional to the number of ion pairs created by the absorbed x-ray.
Self-developing radiochromic film can provide very high resolution measurements, for dosimetry and profiling purposes, particularly in radiotherapy physics.