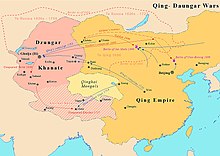
Xinjiang under Qing rule
The Qing sponsored the settlement of millions of ethnic Han Chinese, Hui, Central Asian oasis people (Uyghurs) and Manchu Bannermen in Dzungaria.
[55] The Qing gave the name Xinjiang to Dzungaria after conquering it, with 1 million mu (17,000 acres) being turned from steppe grassland to farmland from 1760 to 1820 by the new colonies of Han Chinese agriculturalists.
[63] Han migration to Xinjiang was permitted by the Manchu Qianlong Emperor, who also gave Chinese names to cities to replace their Mongol names, instituting civil service exams in the area, and implementing the county and prefecture Chinese style administrative system, and promoting Han migration to Xinjiang to solidify Qing control was supported by numerous Manchu officials under Qianlong.
[64] A proposal was written in The Imperial Gazetteer of the Western Regions (Xiyu tuzhi) to use state-funded schools to promote Confucianism among Muslims in Xinjiang by Fuheng and his team of Manchu officials and the Qianlong Emperor.
[71] The Qing portrayed their conquest of Xinjiang in officials works as a continuation and restoration of the Han and Tang accomplishments in the region, mentioning the previous achievements of those dynasties.
[79] Taranchi was the name for Turki (Uyghur) agriculturalists who were resettled in Dzhungaria from the Tarim Basin oases ("East Turkestani cities") by the Qing dynasty, along with Manchus, Xibo (Xibe), Solons, Han and other ethnic groups in the aftermath of the destruction of the Dzhunghars.
[85] The Manchu garrisons were supplied and supported with grain cultivated by the Han soldiers and East Turkestani (Uyghurs) who were resettled in agricultural colonies in Dzungaria.
[110][111] The Qing dynasty gave large amounts of land to Chinese Hui Muslims and Han Chinese who settled in Dzungaria, while Turkic Muslim Taranchis were also moved into Dzungaria in the Ili region from Aqsu in 1760, the population of the Tarim Basin swelled to twice its original size during Qing rule for 60 years since the start, No permanent settlement was allowed in the Tarim Basin, with only merchants and soldiers being allowed to stay temporarily,[112] up into the 1830s after Jahangir's invasion and Altishahr was open to Han Chinese and Hui (Tungan) colonization, the 19th century rebellions caused the population of Han to drop, the name "Eastern Turkestan" was used for the area consisting of Uyghuristan (Turfan and Hami) in the northeast and Altishahr/Kashgaria in the southwest, with various estimates given by foreign visitors on the entire region's population- At the start of Qing rule, the population was concentrated more towards Kucha's western region with around 260,000 people living in Altishahr, with 300,000 living at the start of the 19th century, one tenth of them lived in Uyghuristan in the east while Kashgaria had seven tenths of the population.
The invasion by Jahangir Khoja was preceded by another Qing official, Binjing, who extorted bribes on a massive scale and raped a Muslim daughter of the Kokan aqsaqal from 1818 to 1820.
In 1827, southern part of Xinjiang was retaken by former ruler's descendant Jihangir Khojah; Chang-lung, the Chinese general of Hi, recovered possession of Kashgar and the other revolted cities in 1828.
[130] A revolt in 1829 under Mohammed AH Khan and Yusuf, brother of Jahangir Khoja, was more successful, and resulted in the concession of several important trade privileges to the district of Alty Shahr (the "six cities").
[131] During the 1826 invasion Jahangir Khoja's forces took six Hui Muslims as slaves, Nian Dengxi, Liu Qifeng, Wu Erqi, Ma Tianxi, Tian Guan, and Li Shengzhao, and sold them off in Central Asia, they escaped and fled back to China via Russia.
In Ili the Chinese responded by calling up a massive army of northern and eastern steppe nomads and Hui Muslims (Dongans) numbering 80,000 to fight Jahangir.
[145] The Uyghur Muslim Sayyid and Naqshbandi Sufi rebel of the Afaqi suborder, Jahangir Khoja was sliced to death (Lingchi) in 1828 by the Manchus for leading a rebellion against the Qing.
[147] Until 1846 the country enjoyed peace under the just and liberal rule of Zahir-ud-din, the Uyghur governor, but in that year a fresh Khojah revolt under Kath Tora led to his making himself master of the city, with circumstances of unbridled license and oppression.
The great Tungani revolt, or insurrection of the Chinese Muslims, which broke out in 1862 in Gansu, spread rapidly to Dzungaria and through the line of towns in the Tarim basin.
The Tungani troops in Yarkand rose, and (10 August 1863) massacred some seven thousand Chinese, while the inhabitants of Kashgar, rising in their turn against their masters, invoked the aid of Sadik Beg, a Kyrgyz chief, who was reinforced by Buzurg Khan, the heir of Jahanghir, and Yakub Beg, his general, these being despatched at Sadik's request by the ruler of Khokand to raise what troops they could to aid Muslims in Kashgar.
Buzurg Khan delivered himself up to indolence and debauchery, but Yakub Beg, with singular energy and perseverance, made himself master of Yangi Shahr, Yangi-Hissar, Yarkand, and other towns, and eventually declared himself the Amir of Kashgaria.
[148] Yakub Beg ruled at the height of The Great Game era when the British, Russians, and Manchu Qing empires were all vying for influence in Central Asia.
At Turfan, Yakub Beg was trapped between two armies advancing from Urumqi and Pidjam, and if defeated his line of retreat would be greatly exposed to an enterprising enemy.
[188] Turkic Muslims in different areas of Xinjiang held derogatory views of each other such as claiming that Chinese men were welcomed by the loose Yamçi girls.
[191] Many of the young Kashgari women were most attractive in appearance, and some of the little girls quite lovely, their plaits of long hair falling from under a jaunty little embroidered cap, their big dark eyes, flashing teeth and piquant olive faces reminding me of Italian or Spanish children.
He was clad in a new shirt and trousers of flowered pink, his crimson velvet cap embroidered with gold, and as he smiled and salaamed to us I thought he looked like a fairy prince.
Flocks of sheep with tiny lambs, black and white, pattered along the dusty road; here a goat followed its master like a dog, trotting behind the diminutive ass which the farmer bestrode; or boys, clad in the whity-brown native cloth, shouted incessantly at donkeys almost invisible under enormous loads of forage, or carried fowls and ducks in bunches head downwards, a sight that always made me long to come to the rescue of the luckless birds.
They formed a sharp contrast to their Persian sisters, who either sit behind their husbands or have their steeds led by the bridle; and instead of keeping silence in public, as is the rule for the shrouded women of Iran, these farmers' wives chaffered and haggled with the men in the bazar outside the city, transacting business with their veils thrown back.
But I was told that poetic justice had lately been meted out to one of these upholders of the law of Islam, for by mistake he chastised a Kashgari woman married to a Chinaman, whereupon the irate husband set upon him with a big stick and castigated him soundly.
When a Chinaman is called back to his own home in China proper, or a Chinese soldier has served his time in Turkestan and has to return to his native city of Pekin or Shanghai, he either leaves his temporary wife behind to shift for herself, or he sells her to a friend.
If he has a family he takes the boys with him~—if he can afford it—failing that, the sons are left alone and unprotected to fight the battle of life, While in the case of daughters, he sells them to one of his former companions for a trifling sum.
[194] He procured me a Chinese interpreter, Fong Shi, a pleasant and agreeable young Chinaman, who wrote his mother-tongue with ease and spoke Jagatai Turki fluently, and—did not smoke opium.
[225] Sometimes men aged 50 or 40 took young girls as brides in marriages set up by parents and this was criticized by the Uyghur Christian Nur Luke, who abandoned Islam.