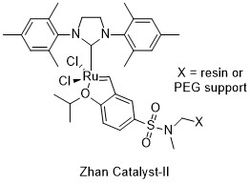
Zhan catalyst
[1] These catalysts are ruthenium complexes with functionally substituted alkoxybenzylidene carbene ligands, which can be chemically bonded to the surface of resins, PEG chains, and polymers.
Like the structurally similar Hoveyda-Grubbs catalyst, they contain an isopropoxystyrene moiety, but include an extra electron-withdrawing sulfonamide group attached to the carbon para to the phenol oxygen.
However, the catalysts containing the tricyclohexylphospine ligand were unstable to air and water, and the catalytic activity is not good enough for some multiple substituted olefin substrates.
Engle, Luo, Houk, Grubbs, and coworkers developed a model that could rationalize initiation rates of ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts with chelated benzylidenes, using a combination of organometallic synthesis, reaction kinetics, NMR spectroscopy, X-ray crystallography, and DFT calculations.
Zhan Catalyst-II is linked to a resin- and PEG-linked support, offering a great advantage in recyclable utility, and leaving little or no trace of metal contamination within the product of olefin metathesis reactions.