Zirconium tetrafluoride
Zirconium(IV) fluoride describes members of a family inorganic compounds with the formula ZrF4(H2O)x.
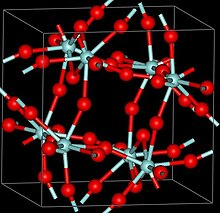
[2] Three crystalline phases of ZrF4 have been reported, α (monoclinic), β (tetragonal, Pearson symbol tP40, space group P42/m, No 84) and γ (unknown structure).
Zirconium dioxide reacts with hydrogen fluoride and hydrofluoric acid to afford the anhydrous and monohydrates: The reaction of Zr metal reacts at high temperatures with HF as well: Zirconium dioxide reacts at 200 °C with solid ammonium bifluoride to give the heptafluorozirconate salt, which can be converted to the tetrafluoride at 500 °C: Addition of hydrofluoric acid to solutions of zirconium nitrate precipitates solid monohydrate.
Hydrates of zirconium tetrafluoride can be dehydrated by heating under a stream of hydrogen fluoride.
The most prominent is potassium hexafluorozirconate, formed by fusion of potassium fluoride and zirconium tetrafluoride:[5] The major and perhaps only commercial application of zirconium fluoride is as a precursor to ZBLAN glasses.