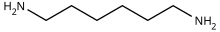
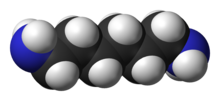
Hexamethylenediamine
The molecule is a diamine, consisting of a hexamethylene hydrocarbon chain terminated with amine functional groups.
The yield is good, but commercially significant side products are generated by virtue of reactivity of partially hydrogenated intermediates.
An alternative process uses Raney nickel as the catalyst and adiponitrile that is diluted with hexamethylenediamine itself (as the solvent).
Otherwise hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) is generated from this diamine by phosgenation as a monomer feedstock in the production of polyurethane.
Such injuries were observed in the accident at the BASF site in Seal Sands, near Billingham (UK) on 4 January 2007 in which 37 persons were injured, one of them seriously.