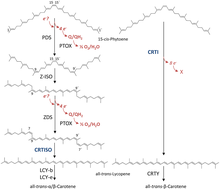
15-Cis-phytoene desaturase
[3][4] This reaction starts a biochemical pathway involving three further enzymes (zeta-carotene isomerase, zeta-carotene desaturase and carotene cis-trans isomerase) called the poly-cis pathway and leads to the red colored lycopene.
[5] PDS converts 15-cis-phytoene into 9,15,9'-tri-cis-ζ-carotene through reduction of the enzymes non-covalently bound FAD cofactor.
The electrons involved in the reaction are subsequently transferred onto plastoquinone[7] and to plastid terminal oxidase PTOX ultimately coupling the desaturation to oxygen reduction.
[10] These inhibitors occupy the binding pocket of plastoquinone within the enzyme thus blocking it from its function.
[1] Due to the clear effect of PDS disruption in plants, the corresponding gene was targeted to showcase successful genome editing in fruit such as apples,[11] grapes[12] or bananas[13] using CRISPR/Cas9 systems.