1810s
Imperialism began to encroach towards African and Asian territories through trade, as the United States saw mass-scaled migration that headed westward towards the American frontier (mostly through the opening of the Oregon Trail.)
Napoleon married Marie-Louise, an Austrian Archduchess, with the aim of ensuring a more stable alliance with Austria and of providing the Emperor with an heir.
The final stage of the War of the Sixth Coalition, the defense of France in 1814, saw the French Emperor temporarily repulse the vastly superior armies in the Six Days Campaign.
Napoleon shortly returned from exile, landing in France on March 1, 1815, marking the War of the Seventh Coalition, heading toward Paris while the Congress of Vienna was sitting.
Already in 1810, the Caracas and Buenos Aires juntas declared their independence from the Bonapartist government in Spain and sent ambassadors to the United Kingdom.
The Spanish Empire in the New World had largely supported the cause of Ferdinand VII over the Bonapartist pretender to the throne in the midst of the Napoleonic Wars.
When Ferdinand's rule was restored, these juntas were cautious of abandoning their autonomy, and an alliance between local elites, merchant interests, nationalists, and liberals opposed to the abrogation of the Constitution of 1812 rose up against the Spanish in the New World.
The arrival of Spanish forces in the American colonies began in 1814, and was briefly successful in restoring central control over large parts of the Empire.
Although Mexico had been in revolt in 1811 under Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla, resistance to Spanish rule had largely been confined to small guerrilla bands in the countryside.
The United States conducted two failed invasion attempts in 1812, first by General William Hull across the Detroit River into what is now Windsor, Ontario, and a second offensive at the Niagara peninsula.
The ending of the war opened a long era of peaceful relations between the United States and the British Empire.
Upon the Persian surrender, the terms of the Treaty of Gulistan ceded the vast majority of the previously disputed territories to Imperial Russia.
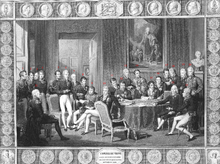
At first, the leading personalities of the system were British foreign secretary Lord Castlereagh, Austrian chancellor Klemens Wenzel, Prince von Metternich and Tsar Alexander I of Russia.
The 1810s continued a trend of increasing commercial viability of steamboats in North America, following the early success of Robert Fulton and others in the preceding years.
[9] Inventor John Stevens' boat, the Juliana, began operation as the first steam-powered ferry October 11, 1811, with service between New York, and Hoboken, New Jersey.
[11] The experience of these vessels, especially that they could now offer a regular service, being independent of wind and weather, helped make the new system of propulsion commercially viable, and as a result its application to the more open waters of the Great Lakes was next considered.
[14] The first commercially successful steamboat in Europe, Henry Bell's Comet of 1812, started a rapid expansion of steam services on the Firth of Clyde, and within four years a steamer service was in operation on the inland Loch Lomond, a forerunner of the lake steamers still gracing Swiss lakes.
"Tug", the first tugboat, was launched by the Woods Brothers, Port Glasgow, on November 5, 1817; in the summer of 1817 she was the first steamboat to travel round the North of Scotland to the East Coast.
Lord Byron, regarded as one of the greatest British poets and remains widely read and influential, wrote his most well-known work during this decade.



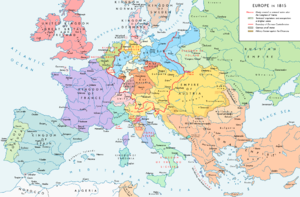
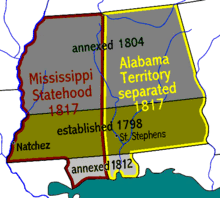
Dec. 10 : Mississippi statehood.