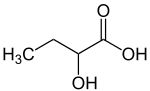
2-Hydroxybutyric acid
2-Hydroxybutyrate, the conjugate base of 2-hydroxybutyric acid, is produced in mammalian tissues (principally hepatic) that catabolize L-threonine or synthesize glutathione.
Oxidative stress or detoxification demands can dramatically increase the rate of hepatic glutathione synthesis.
Under such metabolic stress conditions, supplies of L-cysteine for glutathione synthesis become limiting, so homocysteine is diverted from the transmethylation pathway forming methionine into the transsulfuration pathway forming cystathionine.
Chronic shifts in the rate of glutathione synthesis may be reflected by urinary excretion of 2-hydroxybutyrate.
α-hydroxybutyrate may be useful as an early indicator of insulin resistance in non-diabetic subjects.