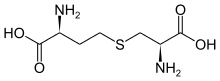
Cystathionine
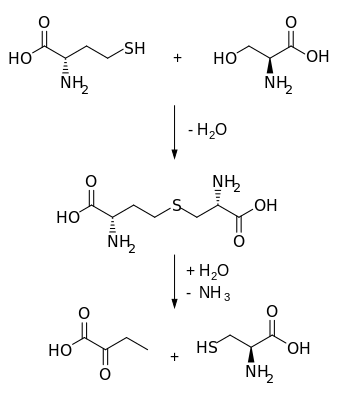
Cystathionine is an intermediate in the synthesis of cysteine from homocysteine.
It is produced by the transsulfuration pathway and is converted into cysteine by cystathionine gamma-lyase (CTH).
It is then cleaved into cysteine and α-ketobutyrate by cystathionine gamma-lyase (lower reaction).
An excess of cystathionine in the urine is called cystathioninuria.
[1] Alternately, the cysteine from the cystathionine gamma-lyase can be used by the enzymes glutamate–cysteine ligase (GCL) and glutathione synthetase (GSS) to produce glutathione.