7-Aminoactinomycin D
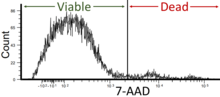
7-Aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD) is a fluorescent chemical compound with a strong affinity for DNA.
It intercalates in double-stranded DNA, with a high affinity for GC-rich regions,[2] making it useful for chromosome banding studies.
Its emission has a very large Stokes shift with a maximum in the deep red: 647 nm.
[4] The related compound actinomycin D is nonfluorescent, but binds DNA in the same way as 7-AAD.
Its absorbance changes when bound to DNA, and it can be used as a stain in conventional transmission microscopy.