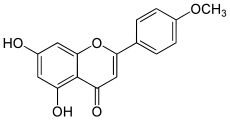
Acacetin
Acacetin is a 4′-O-methylated flavone of the parent compound apigenin, found in Robinia pseudoacacia (black locust), Turnera diffusa (damiana), Betula pendula (silver birch),[1] and in the fern Asplenium normale.
[2] In plant synthesis the enzyme apigenin 4′-O-methyltransferase uses S-adenosyl methionine and 5,7,4′-trihydroxyflavone (apigenin) to produce S-adenosylhomocysteine and 4′-methoxy-5,7-dihydroxyflavone (acacetin).
It shows moderate aromatase inhibition.
This article about an aromatic compound is a stub.
You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.