Accident analysis
Its retrospective nature means that accident analysis is primarily an exercise of directed explanation; conducted using the theories or methods the analyst has to hand, which directs the way in which the events, aspects, or features of accident phenomena are highlighted and explained.
These analyses are also invaluable in determining ways to prevent future incidents from occurring.
They provide good insight by determining root causes, into what failures occurred that led to the incident.
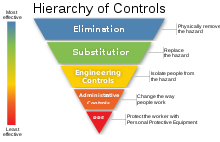
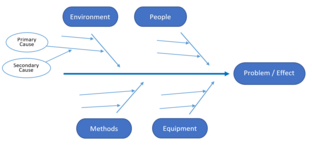
Some common types of these models include the Five Why's model, Ishikawa (fishbone) diagram, the Fault Tree Analysis (FTA), or the Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA).
[4] Once all available data has been collected by accident scene investigators and law enforcement officers, camera matching, photogrammetry or rectification can be used to determine the exact location of physical evidence shown in the accident scene photos.